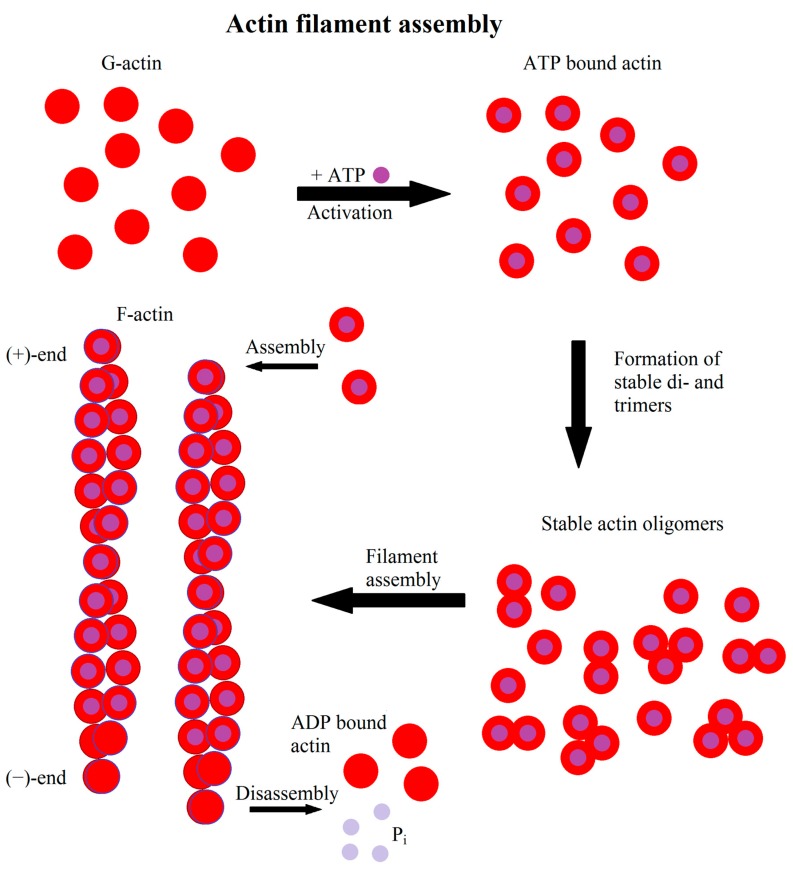
Figure 1.
Scheme of actin filament formation. First G-actin binds to ATP. Afterwards, it forms stable di- or trimers and, finally, filaments elongate by addition of monomers. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP leads to a distinction between the fast growing (+)-end and the slower growing or dissociating (−)-end.