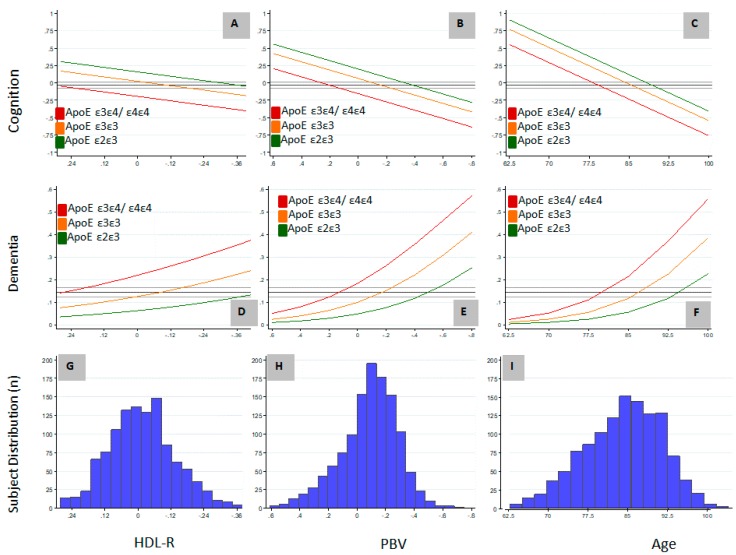
Figure 1.
The association of the distribution of High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) ratio (HDL-R), Plasmalogen Biosynthesis value (PBV) and age with probability of dementia and cognition in Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε2ε3, ε3ε3 and ε3ε4/ε4ε4 carriers. (A) Effect of HDL-R on cognition in different APOE genotypes; (B) Effect of PBV on cognition in different APOE genotypes; (C) Effect of age on cognition in different APOE genotypes; (D) Effect of HDL-R on probability of dementia in different APOE genotypes; (E) Effect of PBV on probability of dementia in different APOE genotypes; (F) Effect of age on probability of dementia in different APOE genotypes; (G) Distribution of HDL-R in the study cohort; (H) Distribution of PBV in the study cohort; (I) Distribution of age in the study cohort. Multiple regression analysis was carried out to determine the association of the distribution of HDL ratio, PBV, and age with dementia and cognition in the study cohort. Cognition was measured as global cognition score (GCOG), which is the average of z-scores from a battery of cognitive measurements. Mean normalized, log10 transformed values of HDL-R, PBV, and mean-centered values of age are in the x-axes. y-axes represent GCOG in the graphs depicting the associations of cognition with HDL-R (A), PBV (B) and age (C); in the graphs depicting dementia (D–F), y-axes represent the probability of dementia as a fraction. In the distribution graphs (G–I), y-axes represent the number of individuals. HDL-R: HDL-C to total cholesterol ratio; PBV: Plasmalogen Biosynthesis value.