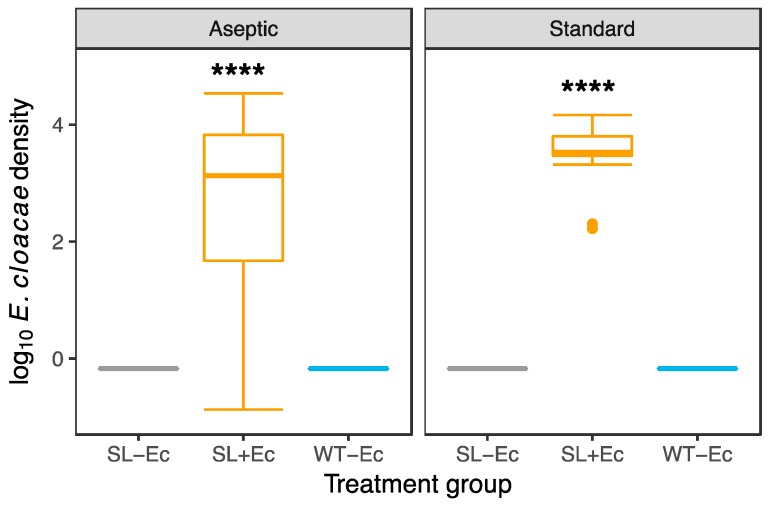
Figure 1.
Culturable bacterial densities in inoculated (SL+Ec) and symbiont-free treatment groups (−Ec) under aseptic and standard conditions. Bacterial densities were assessed in self-limiting (SL) transgenic larva that had Enterobacter cloacae added to their diet (SL+Ec) and compared to SL larva without E. cloacae in their diet (SL−Ec) and wild type (WT) larva without E. cloacae in their diet (WT−Ec). In aseptic conditions, in the SL+Ec treatment, 94 out of 96 larvae were successfully inoculated with JJBC. In standard conditions, all SL+Ec (n = 8) contained the focal symbiont. In both standard and aseptic conditions, treatments that were not inoculated with Ec had bacterial densities of 0 c.f.u./μL (WT−Ec (aseptic: n = 36, standard n = 7) and SL−Ec (aseptic n = 60, standard n = 8). Bacteria in the inoculated larvae were streptomycin resistant and confirmed in morphology to our focal E. cloacae JJBC 11.1B strain. Asterisks indicate that inoculated treatments SL+Ec contain significantly more microbes than uninoculated treatments (p < 0.0001 in Kruskal-Wallis tests).