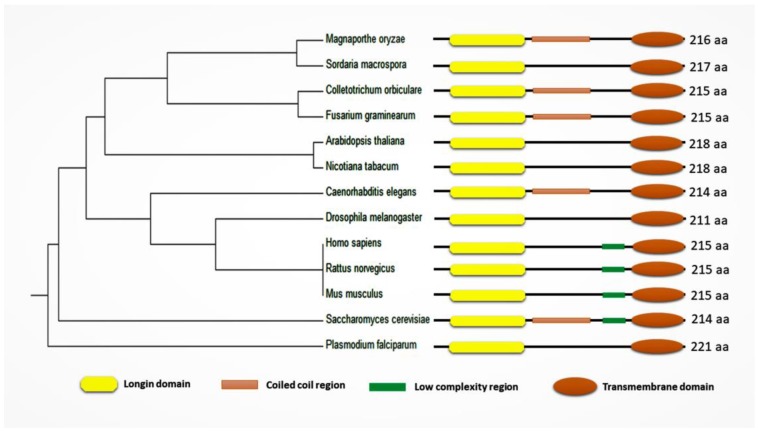
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis and domain characterization of Sec22 and its homologues (Sec22 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its homologues among different organisms including Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, Drosophila melanogaster, Caenorebditis elegans, Plasmodium falciparum, Arabidopsis thaliana, Nicotiana tabacum, Magnaporthe oryzae, Colletotrichum orbiculare, Sordaria macrospora, and Fusarium graminearum). Longin domain is a conserved N-terminal domain with a profilin-like fold which is considered an essential regulator. The coiled-coil region is important in soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) zippering. The low-complexity region may be involved in flexible binding associated with specific functions. The transmembrane domain is a typical stretch of hydrophobic residues located at the C-terminus, involved in anchoring the protein to the membrane and participating in other aspects of the functions of these proteins.