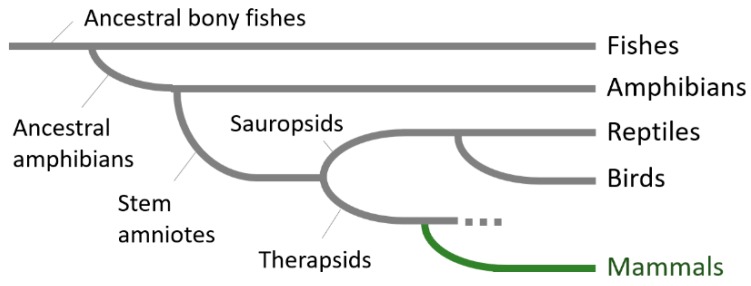
Figure 1.
A phylogenetic tree of vertebrate evolution. A diagram showing the lines of evolutionary descent of different vertebrates from a common ancestor. The ancestral bony fish gave rise to ancestral amphibians. Through water-land transition, ancestral amphibians gave rise to stem anamniotes, which then separately evolved into sauropsids and therapsids. Sauropsids are not only the ancestors of existing reptiles but also gave rise to the ancestors of birds. Mammalian species have evolved from therapsid ancestors, although many groups of the therapsids have become extinct (dashed line). The six-layered cortex was inherited by the mammalian ancestor of therapsids (green line) more than 200 million years ago [10]. Modified from Jarvis et al. [11].