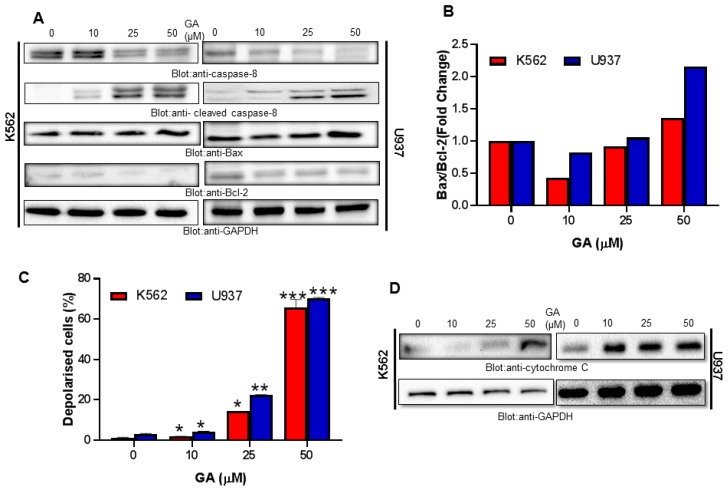
Figure 5.
Greensporone A-induced mitochondrial signaling pathways in leukemic cells. Greensporone A treatment causes alteration in Bcl-2 expression. (A) K562 and U937 cells were treated with increasing doses of greensporone A for 24 h, as indicated. After cell lysis, equal amounts of proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE, transferred to PVDF membrane, and immunoblotted with antibodies against caspase-8, cleaved caspase-8, Bax, Bcl-2, and GAPDH. (B) Data obtained from immunoblot analysis of Bax and Bcl-2 in K562 and U937 were used to evaluate effects of GA on Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Densitometric analysis of Bax and Bcl-2 bands was performed using AlphaImager Software (San Leandro, CA, USA), and data (relative density normalized to b-actin) were plotted as Bax / Bcl-2 ratio. Treatment with greensporone A caused loss of mitochondrial membrane potential in leukemic cells. (C) K562 and U937 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of greensporone A for 24 h and analyzed by Muse analyzer described in Section 2. The graph displays the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001). Greensporone A-induced the release of cytochrome c. (D) K562 and U937 cells were treated in the presence and absence of greensporone A for 24 h. Cytoplasmic fraction was isolated as described in Section 2. Cell extracts were separated on SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membrane, and immunoblotted with an antibody against cytochrome c and GAPDH.