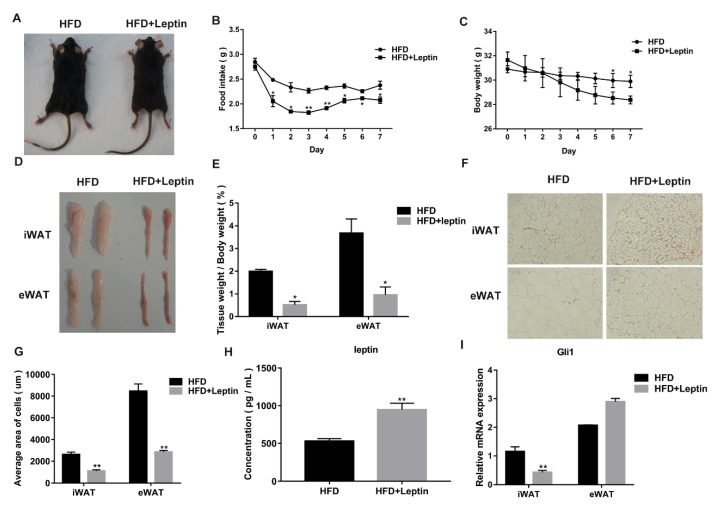
Figure 2.
Leptin decreases food intake and adipose weight of high fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice by inhibiting the Hh signaling pathway. (A) Representative image of HFD-fed mice injected with leptin recombinant protein or the control for seven days. (B,C) Daily food intake and body weight of the mice in the control and leptin recombinant protein injection groups (n = 4–6 per group). (D) Representative images of inguinal and epididymal white adipose tissue (iWAT and eWAT, respectively) injected with leptin recombinant protein or the control for seven days. (E) White adipose tissue masses were determined relative to body weight from HFD-fed mice injected with leptin recombinant protein or the control (n = 5). (F) Representative images of white adipose (iWAT and eWAT) stained with HE from HFD-fed mice injected with leptin recombinant protein or the control (n = 3). (G) Every adipose cell area in the eWAT and iWAT sections stained with HE in HFD-fed mice injected with leptin recombinant protein or the control (n = 3). (H) Serum leptin concentration was detected by ELIAS kit after injecting with leptin recombinant protein or the control (n = 5). (I) RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression level of the Hh signaling pathway marker gene Gli1 in eWAT and iWAT after injecting with leptin recombinant protein or the control. Scale bar = 20 μm. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.