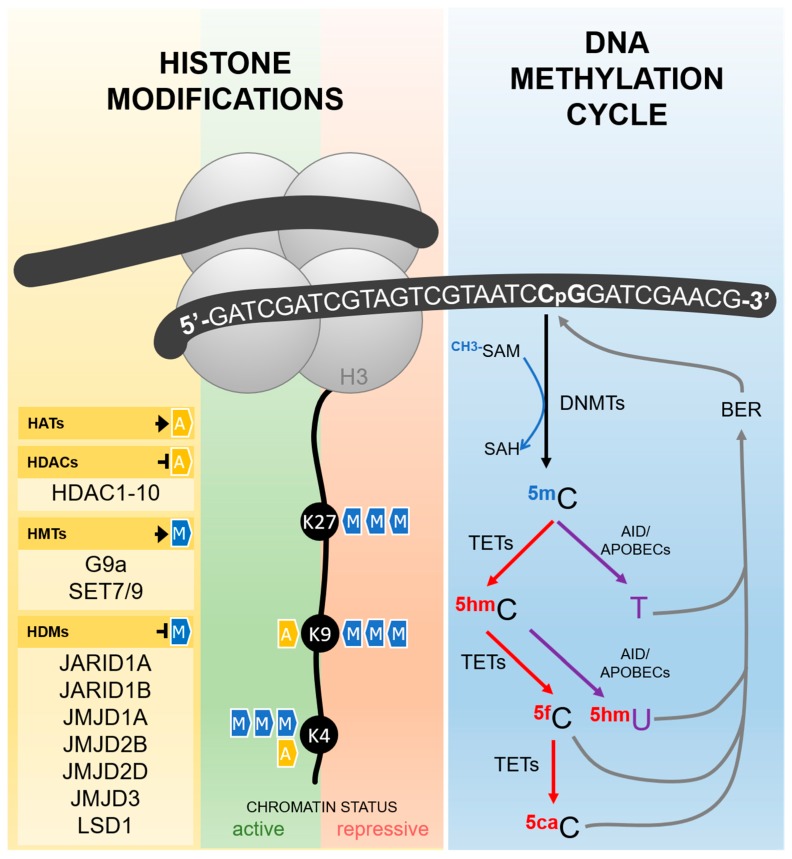
Figure 1.
Epigenetic mediators involved in the establishment and erasure of histone post-translational modifications and DNA methylation, as described in the text. Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are responsible for the transfer of an acetyl group to different histone amino acid residues, including lysines 4 and 9 (K4 and K9). Histone deacetylases (HDACs) catalyze the removal of this group. Methyl groups can also be added to different amino acids in the tails of the histones by histone methyltransferases (HMTs) and removed by histone demethylases (HDMs). Histone acetylation always results in an active chromatin status, while the effects of histone methylation depends on the number of groups added and the amino acid residue involved. As exemplified in the figure, H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 are repressive marks, while H3K4me3 is an active mark. DNA methylation takes place more frequently in cytosines followed by guanines in the so-called CpG sites, reaction catalyzed by DNA-methyltransferases (DNMTs) using S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as methyl donor. The erasure of DNA methylation can be driven by an active pathway, either by sequential oxidations or deamination. In the oxidation pathway (depicted in red), Ten-eleven translocation enzymes (TETs) catalyze the conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), which is further oxidized to form 5-formylcytosine (5fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC). Both 5fC and 5caC are recognized by the base excision repair (BER) machinery and removed from the DNA strand, resulting in the reincorporation of a non-methylated cytosine. In the deamination pathway (depicted in purple), 5mC and 5hmC can be deaminated by AID/APOBEC (Activity Induced Deaminase/Apolipoprotein B mRNA Editing Catalytic Polypeptide-like) family of enzymes, generating thymine and 5-hydroxymethyluracil (5hmU), respectively. The mispairing of these bases with guanine in the opposite strand activates the BER machinery and results in the reincorporation of a non-methylated cytosine. G9a: histone methyltransferase G9a; SET7/9: histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD7; JARID: Jumonji/ARID Domain-Containing Protein; JMJD: Jumonji Domain-Containing Protein; LSD1: Lysine-specific demethylase 1; SAH: S -adenosylhomocysteine.