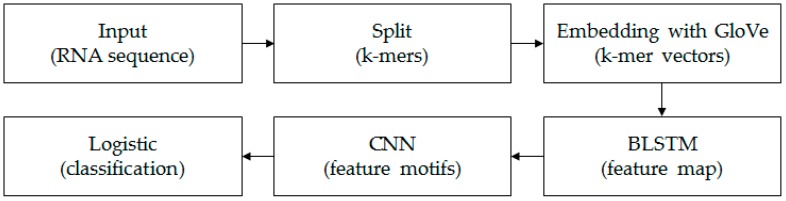
Figure 1.
The structure diagram of the model. We first split each input RNA sequence into k-mers using a moving window approach [21]. Then, based on all k-mer sequences, all the k-mer embedding vectors were learned by the unsupervised GloVe method. The embedding layer embedded all k-mers into the vector space and turned the k-mer sequence into a real matrix. The BLSTM layer consisted of two LSTMs layers that were parallel but opposite in direction, to capture long-term dependency information between sequences. The following CNN with three convolution layers scanned the above results using multiple convolutional filters to obtain different features. The final fully connected layer and logistic acted as classifiers to get the probability and final classification result of the input sequence belonging to a positive or negative class.