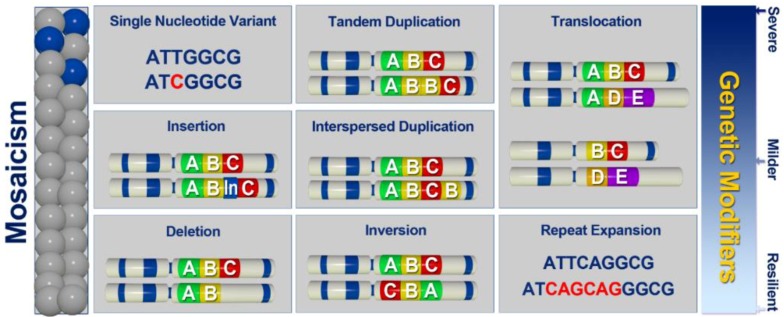
Figure 2.
Uncovering missing heritability. A spectrum of variants, beyond the SNVs (single nucleotide variants), contributes to human genetic conditions as either germline or somatic variations. In addition, different types of variants, such as large insertions (including mobile element insertions (MEI)), deletions, duplications, as well as translocations, inversions, repeat expansions and other complex changes may be the source of genetic modifiers with the capacity to alleviate or exacerbate the effect of the primary pathogenic variant, and thus contribute to phenotypic variability (severe-mild-none).