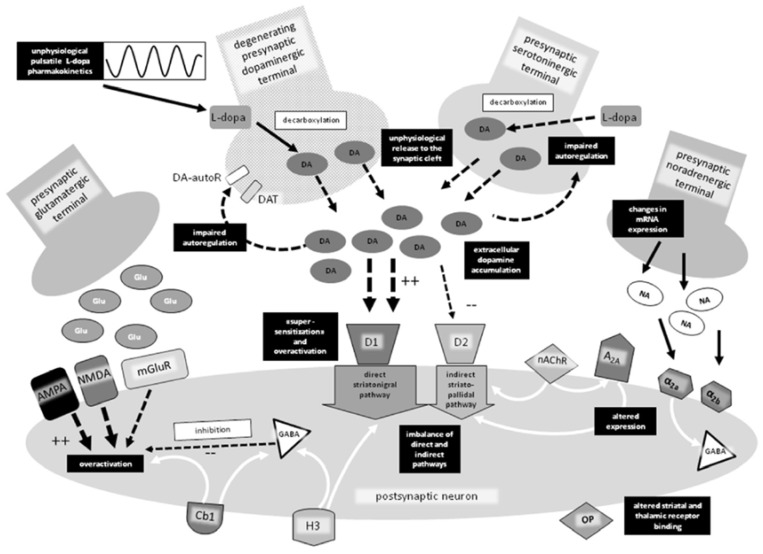
Figure 19.
Pathophysiology of levodopa-induced dyskinesia (Reprinted with permission from Springer Nature: Springer CNS Drugs Pharmacological Strategies for the Management of Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease, Schaeffer, E.; Pilotto, A.; Berg, D., 2014, doi: 10.1007/s40263-014-0205-z. [360]).  Physiological activation,
Physiological activation,  pathological alterations in LD-induced dyskinesia (LID),
pathological alterations in LD-induced dyskinesia (LID),  pathological alterations in LID,
pathological alterations in LID,  modulation, ++ increased activation, -- decreased activation. A2A adenosine receptor, α2a and α2ab noradrenergic receptors, AMPA α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid, Cb1 cannabinoid receptor, D1 and D2 dopaminergic receptors, DA dopamine, DA-autoR dopamine autoreceptor, DAT dopamine transporter, GABA γ-aminobutyric acid, Glu glutamate, H3 histamine receptor, LID levodopa-induced dyskinesia, mGluR metabotropic glutamate receptor, NA noradrenaline, nAchR nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, NMDA N-methyl-D-aspartate, OP opioid receptor.
modulation, ++ increased activation, -- decreased activation. A2A adenosine receptor, α2a and α2ab noradrenergic receptors, AMPA α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid, Cb1 cannabinoid receptor, D1 and D2 dopaminergic receptors, DA dopamine, DA-autoR dopamine autoreceptor, DAT dopamine transporter, GABA γ-aminobutyric acid, Glu glutamate, H3 histamine receptor, LID levodopa-induced dyskinesia, mGluR metabotropic glutamate receptor, NA noradrenaline, nAchR nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, NMDA N-methyl-D-aspartate, OP opioid receptor.