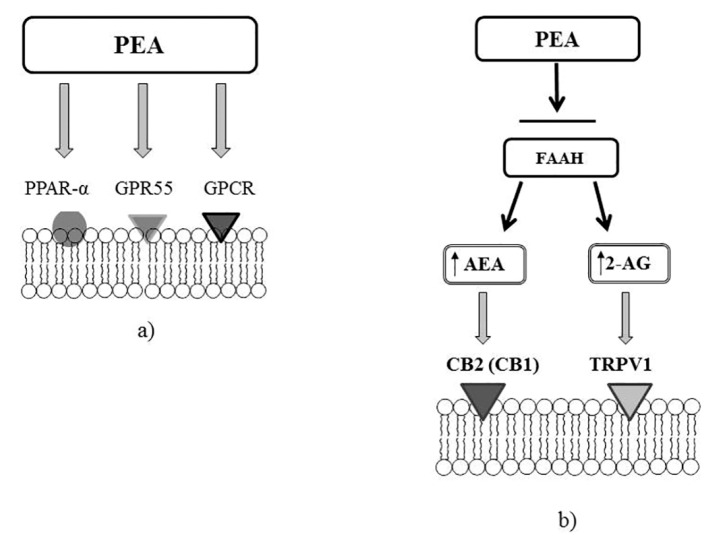
Figure 3.
Molecular targets of PEA. (a) PEA can directly activate G protein-coupled receptor α (PPARα) or a cannabinoid receptor G protein-coupled receptor (GPR55). (b) PEA through the inhibition of the expression of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), may increase the endogenous levels of AEA and 2-AG, which directly activate cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) (or cannabinoid receptor 1, CB1) and transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) channels.