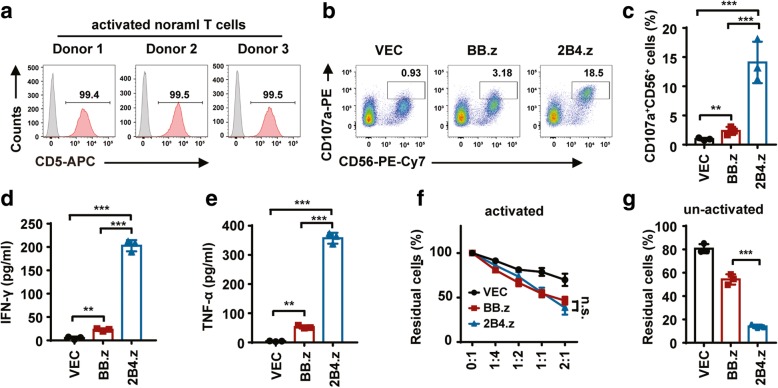
Fig. 5.
Both BB.z-NK and 2B4.z-NK present side effects on CD5+ normal T cells. a Flow cytometry analysis showing the proportion of CD5+ cells in donors’ normal T cells. b Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the proportion of CD107a+CD56+ cells after co-incubation with activated normal T cells as E:T = 1:3 for 5 h. c Quantification and statistical analysis of the data in b (n = 3; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). d ELISA data showing the release of IFN-γ by NK cells after co-incubation with activated normal T cells for 12 h (n = 3; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). e ELISA data showing the release of TNF-α by NK cells after co-incubation with activated normal T cells for 12 h (n = 3; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). f Direct cytotoxicity of CAR-NK against activated normal T cells. Activated normal T cells and CAR-NK cells or VEC-NK cells were cocultured for 6 h at the indicated E:T ratio. Flow cytometry analysis of the proportion of CD5+CD56− cells (n = 3; n.s., no significance). g Direct cytotoxicity of CAR-NK against un-activated normal T cells. Un-activated normal T cells and CAR-NK cells or VEC-NK cells were cocultured for 6 h at the E:T ratio of 1:1. Flow cytometry analysis of the proportion of CD5+CD56− cells (n = 3; ***p < 0.001). VEC: VEC-NK; BB.z: BB.z-NK; 2B4.z: 2B4.z-NK