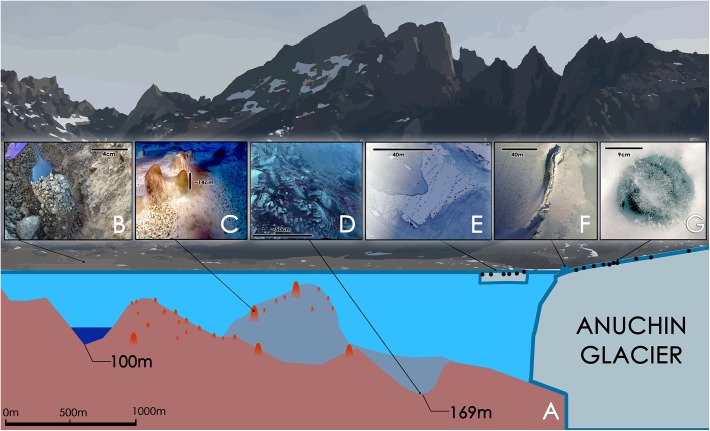
FIGURE 2.
(A) Schematic illustration of Lake Untersee with its 169 m oxic basin and a 100 m anoxic basin [illustration based on (Wand et al., 2006)]. (B) Soil sample. (C) Large conical stromatolites, pinnacle mats and flat mats at a depth of about 24 m. The scale bar is an estimate. (D) Pigmented microbial benthic mats at a depth of 169 m. The scale is an estimate. The pink dots are artifacts that were introduced during a white balance correction. They may indicate a similar surface color as seen in C. (E) “White Ice Patch” – glacial ice integrated in the lake ice containing cryoconite holes that are aligned from NE to SW; the image is oriented with North toward the top of the image. (F) Aerial image of a pressure ridge formed by the Anuchin Glacier (left) at the glacier-lake ice interface. Cryoconite holes are visible as dark dots in the glacier ice. The top left corner is orientated toward north. (G) Typical morphology of an Antarctic ice-lidded cryoconite hole.