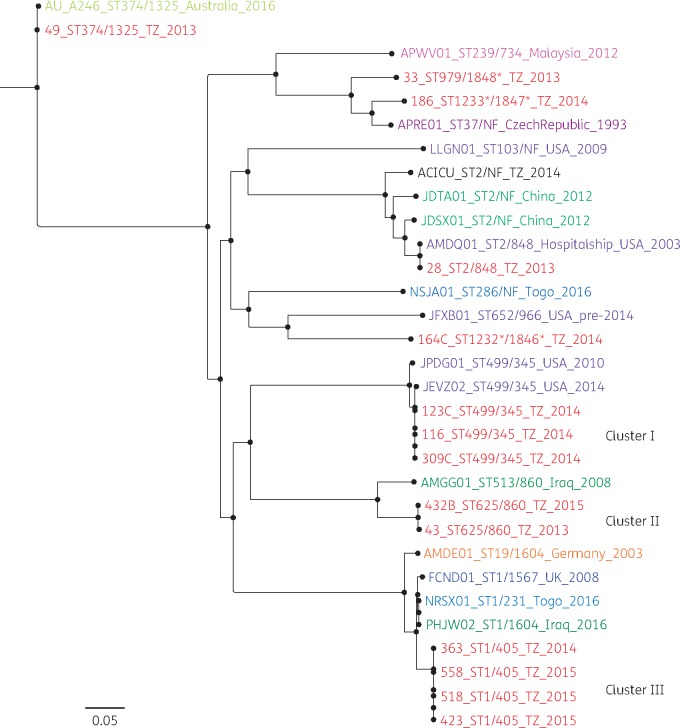
Figure 1.
SNP phylogeny analysis of 31 A. baumannii genomes that were isolated in 10 countries: Tanzania (TZ; current study), USA, UK, China, Malaysia, Togo, Australia, Czech Republic, Iraq and Germany. From the SNP phylogenetic tree, three clusters for Tanzanian isolates were observed. Cluster I was composed of three isolates with ST499/345 as per Pasteur/Oxford schemes. All had the T82S mutation in gyrA and had no mutations in parC. Isolates from this cluster possessed pIOMTU433-like plasmids, which contained several antibiotic resistance genes, and pAC450, which did not carry any resistance genes. Cluster II was composed of two isolates with ST625/860 as per Pasteur/Oxford schemes. Both isolates were isolated in the surgical ICU B ward. They both had fluoroquinolone mutations S81L and S84L in gyrA and parC, respectively, and were ciprofloxacin resistant and nalidixic acid resistant. The isolates contained more than one plasmid with no resistance genes on them with the exception of two: pA297-1, which carried aadB; and pKCRI-43-1, containing the genes floR and sul2. Cluster III was composed of four isolates with ST1/405 as per Pasteur/Oxford schemes. They all had fluoroquinolone mutations S81L and S84L in gyrA and parC, respectively. They were all resistant to ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid. Three possessed a novel plasmid and one possessed plasmid pAB14 containing blaOXA-23.