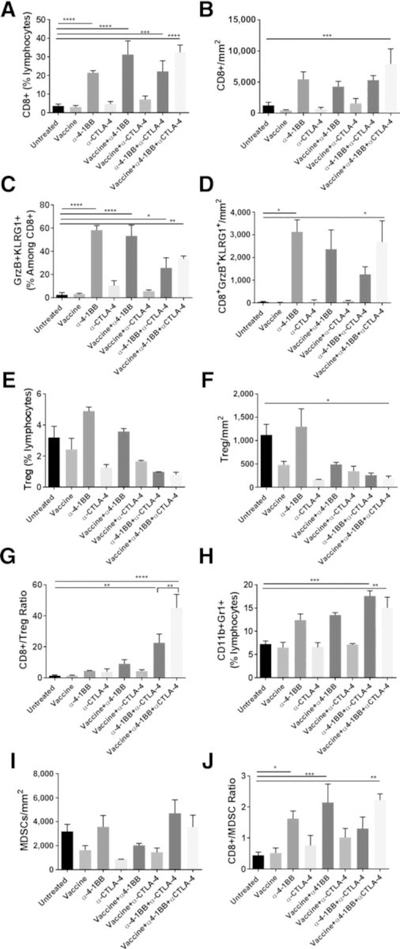
Figure 4.
Combination of α4–1BB and αCTLA-4 provides tumor protection by increasing the ratios of CD8+ T cells to immunosuppressive populations. Mice bearing subcutaneous mEER tumors were either untreated or treated with intranasal HPV peptide vaccine, α4–1BB, or αCTLA-4 individually or in combinations as described in Fig. 1 legend. Tumors were harvested at day 15 and the isolated leukocytes were characterized by flow cytometry after staining for different surface and intracellular markers. The figure shows percentages of CD8+T cells (A), frequencies of CD8+ T cells as number of cells per tumor area (B), percentages of CD8+ T cells expressing GrzB and KLRG1 (C), frequencies of CD8+GrzB+KLRG1+ cells (D), percentages of CD4+FoxP3+ Tregs (E), frequencies of CD4+FoxP3+ Tregs (F), CD8+ T cells to Treg ratio (G), percentages of CD11b+Gr1+ MDSCs (H), frequencies of CD11b+Gr1+ MDSCs (I), and the CD8+ T cells to MDSC ratio (J). Data are represented as means ± SEM. Results represent pooled data from multiple experiments (n = 2–11 mice/group). Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005; ****, P < 0.00005.