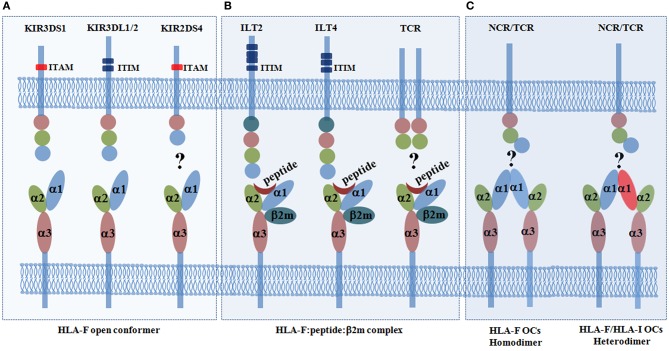
Figure 1.
Immune receptors for the human leukocyte antigen (HLA-F) open conformer (OC) and HLA-F:peptide:β2m complex. (A) HLA-F OCs can be recognized with the highest affinity by the activating receptor KIR3DS1 and can be recognized by the inhibitory receptors KIR3DL1/2. However, the results regarding the interaction of the HLA-F OC and the activating receptor KIR2DS4 are disputed (27, 28, 30, 31). (B) The HLA-F:peptide:β2m complex can only be recognized by the inhibitory receptors immunoglobulin (Ig)-like transcript receptor 2 (ILT2) and ILT4 (29, 30). However, whether there are HLA-F peptide-restricted T cell receptors (TCRs) is not yet known (30). (C) HLA-I OCs can be expressed on the cell surface as homodimers (43), and it has been postulated that HLA-I/HLA-F heterodimers can form (44). Whether HLA-F can be recognized by other TCRs or natural killer cell receptors (NCRs) remains to be explored. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed on natural killer (NK) cells and on subpopulations of T cells. KIRs have either two (2D) or three (3D) extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains and different cytoplasmic tails (short or long). Inhibitory KIRs have long cytoplasmic tails (L) that contain immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs). Activating KIRs have short cytoplasmic tails (S) that lack ITIMs but associate with the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM), such as the adapter DAP12, via a positively charged arginine or lysine residue in their transmembrane domain. Immunoglobulin-like transcript 2 (ILT2, also known as CD85j and LIR1) has four extracellular Ig-like domains and four cytoplasmic ITIMs. ILT4 (also known as CD85d and LIR2) has four extracellular Ig-like domains and three cytoplasmic ITIMs. TCRs (T cell receptors) recognize peptides presented by HLA molecules.