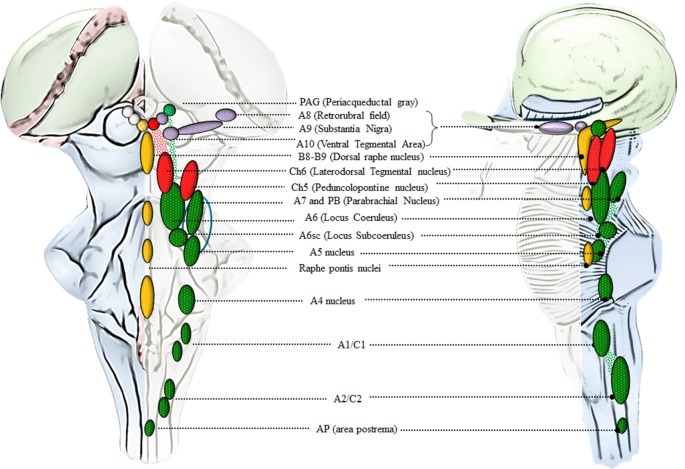
Figure 2.
An anatomical overview of the brainstem reticular formation (RF). This cartoon provides a synthetic overview of the neuroanatomy of brainstem RF nuclei in order to foster orientation within the brainstem when referring to the site-specificity of the effects induced by AMPHs. Monoamine-containing nuclei are placed in a quite restricted brain region corresponding to the median and lateral column of the brainstem RF. In detail, the median column hosts 5-HT-containing nuclei (yellow), which extend along the medulla and pons to reach the mesencephalon at the level of the periaqueductal gray (PAG). 5-HT containing nuclei at this level represent the rostral extent of the dorsal raphe nucleus (B8-B9). Since an analysis of 5-HT neurons in the effects of AMPHs is beyond the scope of the present review article, we focus on the dorsal raphe nucleus just concerning the PAG region, which contains catecholamine neurons. In fact, the PAG hosts a mixed population of catecholamine and acetylcholine (ACh)-containing nuclei which are placed in the lateral column of the RF. This is the case of DA (violet), NE (green) and ACh (red) nuclei which represent the rostral extent of A10 Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA), A6 (LC) and CH6, respectively. Moving downstream to the mesencephalic DA nuclei (A8, A9, A10), a constellation of nuclei appears within the lateral column of RF. These include the two pontine ACh nuclei (Ch5 and Ch6) and a number of NE nuclei placed along the ponto-medullary RF, namely A6 (LC), A6sc (subcoeruleus), A7 which intermingles with NE neurons of the rostral PB nucleus (here represented as a continuum), A5, A4, and two mixed NE/E-containing groups in the medulla, namely A1/C1 [rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM)] and A2/C2 (dorsomedial cell group), which extends towards the obex within the AP (area postrema). The A7 neurons together with PB-NE neurons and the A5 nucleus contribute to define the Kolliker-Fuse nucleus (blue circle, Milner et al., 1986; Byrum and Guyenet, 1987). The A6 nucleus together with the A6sc, the medial PB in the rostral pons and the epicoeruleus nucleus within the PAG, constitute the LC complex.