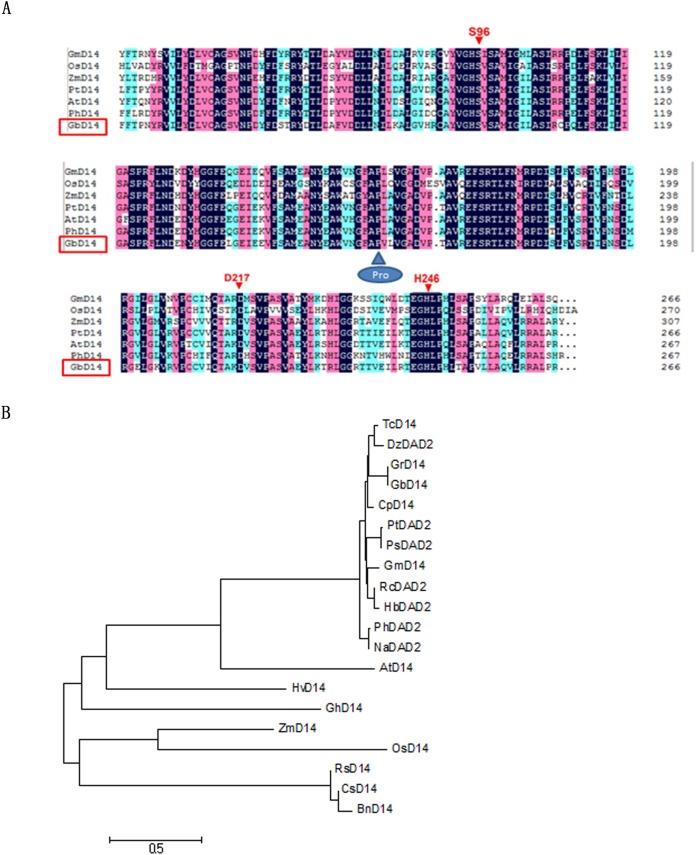
Figure 1. Characterization of GbD14.
(A) Amino acid sequence alignment of GbD14 and other D14 (DAD2) proteins from other plant species, as performed by DNAMAN software. Identical amino acids are highlighted in blue. Three conserved amino acid sites (Ser96, Asp217, His246) are indicated by red arrows. (B) Phylogenetic relationship of the above D14 (DAD2) proteins. The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbour-joining method. The analysis involved 20 amino acid sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 212 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted via MEGA7.