Fig. 8.
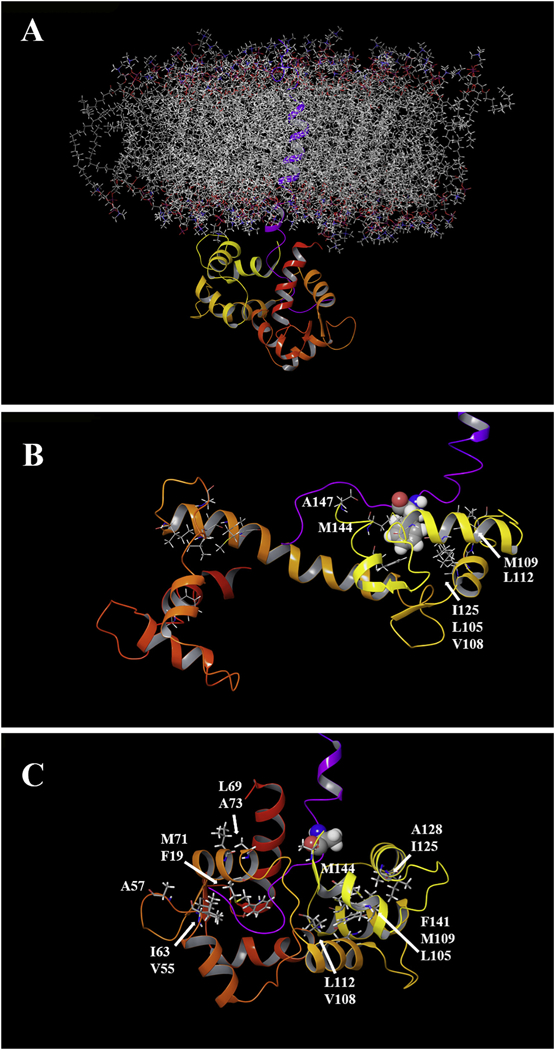
Computer modeling of Ca2+/CaM and CH3MUA-SFWT embedded in a lipid bilayer. A: The transmembrane and short form cytoplasmic domains of CEACAM1 (purple trace) were embedded in a POPC lipid bilayer and the cytoplasmic domain docked to the C-terminal domain of Ca2+/CaM (see Methods). B: The key residue Phe-454 (space filling) of CEACAM1 is shown in close proximity with hydrophobic clusters of Ca2+/CaM in the C-lobe C: A model of the F454A mutant in close proximity to hydrophic clusters in both lobes of Ca2+/CaM.
