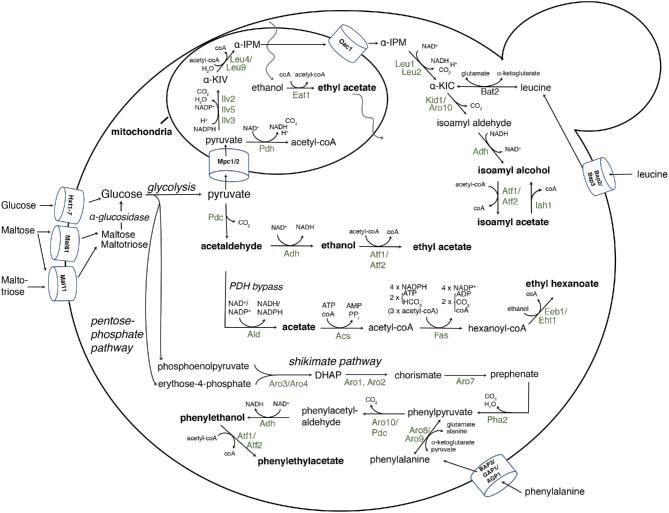
Figure 5.
An overview of the yeast enzymes leading to isoamyl alcohol, 2-phenylethanol and esters during alcoholic fermentation. For simplicity, biochemical pathways leading to fusel alcohols are only shown for isoamyl alcohol and for esters only for isoamyl acetate, ethyl acetate and ethyl hexanoate. The pathways leading to active amyl alcohol and isobutanol also occur via the mitochondrial ILV (leucine-isoleucine-valine) pathway through Ilv2, 5 and 3, or via degradation of the amino acids isoleucine and valine by Bat1 and Bat2. The enzymes shown are indicated in their host organelles or in the cytosol and with the balance of the co-factors, substrates and byproducts in the biochemical reactions. Pyruvate originates from glycolysis. l-Leu4 and s-Leu4 indicate the long and short isoform present in the mitochondria and the cytosol, respectively, whereas Leu9 is a mitochondrial Leu4 paralog. α-KIV, α-ketoisovalerate; α-IPM, α-isopropylmalate; α-KIC, α-ketoisocaproate; ACS, Acetyl-coA synthase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; FAS, fatty acid synthase complex; PDC, pyruvate decarboxylase; ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; ALD, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase; DAHP, 3- deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate.