FIGURE 5.
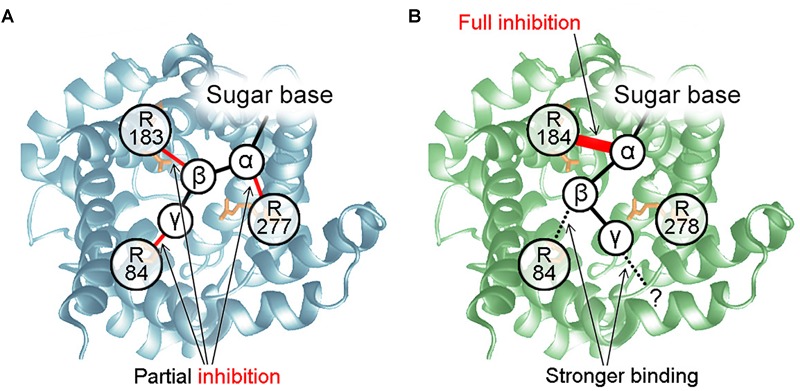
Mechanisms of UCP-PN interaction and inhibition. (A) PN inhibition mechanism for UCP1. The α-, β-, and γ-phosphate of PNs bind to R277, R183, and R84, respectively. R84 does not interact with the β-phosphate of diphosphate-PNs. The three P-R bonds additively contribute to maximum inhibition but interact independently. None of them is essential for inhibition or PN binding. (B) Mechanism of UCP3 inhibition by PNs. R184 and R84 bind to the α-and β-phosphate of PNs. Interaction between R184 and the PN α-phosphate is essential for protein inhibition and may induce a conformational change. Interaction of R84 with the β-phosphate increases binding strength. Instead of R278, another residue is proposed to be a part of the UCP3 PN-binding-pocket, which binds to the γ-phosphate of PN.
