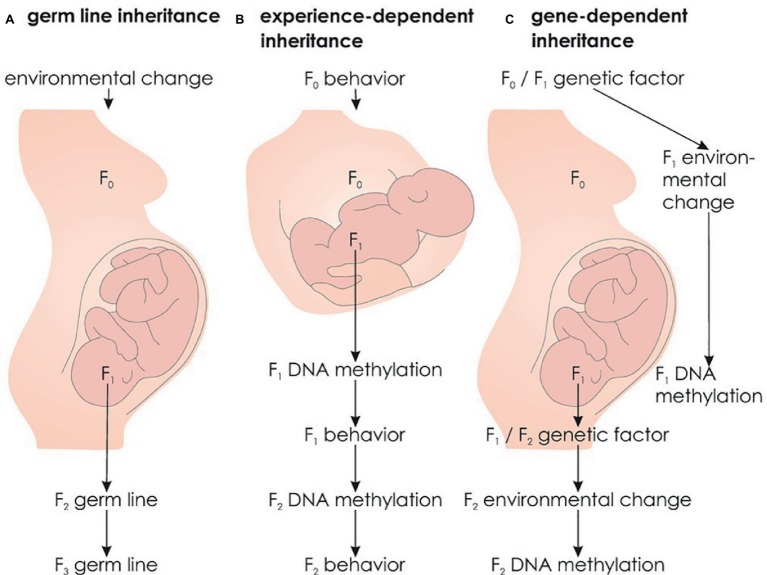
Figure 5.
Alternative forms of transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. (A) Germ line epigenetic inheritance: An environmental factor acts on the F0 generation and induces an epigenetic state that is transmitted to subsequent, unaffected individuals via the germ line. (B) Experience-dependent epigenetic inheritance: Maternal behavior induces an epigenetic state in the offspring (F1) that in turn influences F1 behavior toward its offspring (F2) transmitting behavior and epigenetic states across generations. (C) Gene-dependent epigenetic inheritance: A genetic factor modulates the probability of an environmental factor that influences F1 epigenetic states. As F1 likely transmits the genetic factor to F2, epigenetic states are transmitted across generations.