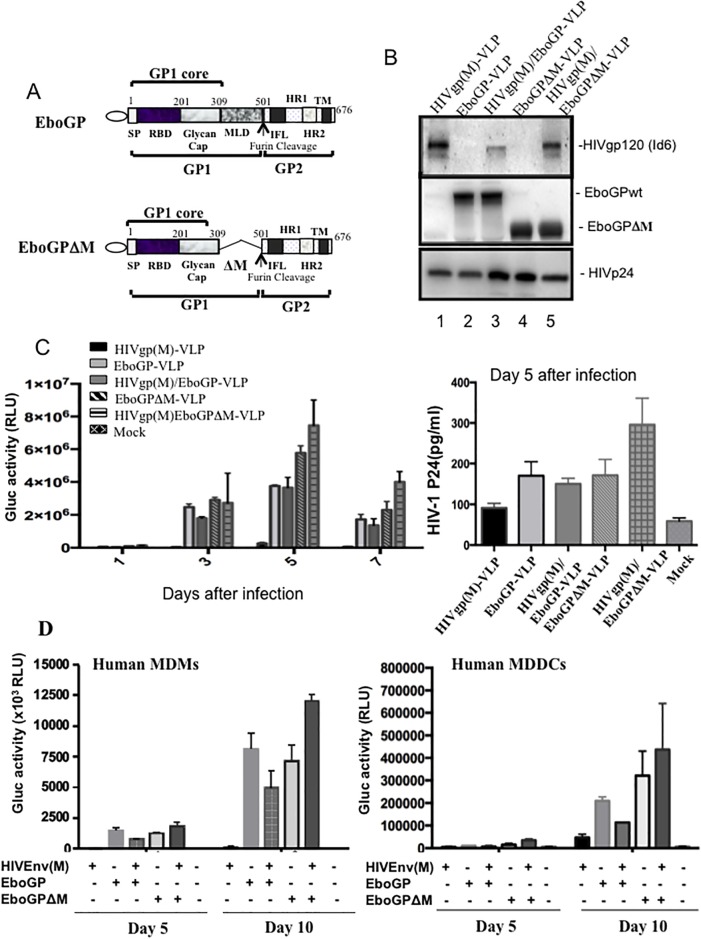
Fig 2. The EboGPΔM incorporation into HIV VLPs mediates more efficient virus entry in MDMs and MDDCs than EboGP.
A) Schematic diagram of the peptide sequence for EboGPwt and EboGPΔM, which contained a deletion of the MLD region. SP: signal peptide; RBD: receptor binding domain; MLD: mucin-like domain; IFL: internal fusion loop; HR1, HR2: heptadrepeat1/2; TM: transmembrane domain. B) Analysis of the viral compositions of various VLPs produced from 293T cells co-transfected with HIV Env(M) and/or EboGP/EboGPΔM expressing plasmids, and HIV CMVin-Gag/Pol and HxΔRI/ΔE/Gluc. Viral compositions were analyzed by WB with anti-HIVgp, anti-EboGP antibody or anti-HIVp24 antibody C) THP1 cells were infected by various HIVgp and/or EboGPwt/ΔM pseudotyped HIV VLPs. At 1, 3, 5, and 7 days post-infection, the supernatants were collected and subjected to Gluc activity and p24 ELISA assay. D) Human MDMs (left panel) or human MDDCs (right panel) were infected by various HIVgp and/or EboGPwt/ΔM pseudotyped HIV VLPs and Gluc activity was monitored at 5 and 10 days post-infection. Error bars represent variation between duplicate samples, and the data is representative of results obtained in two independent experiments.