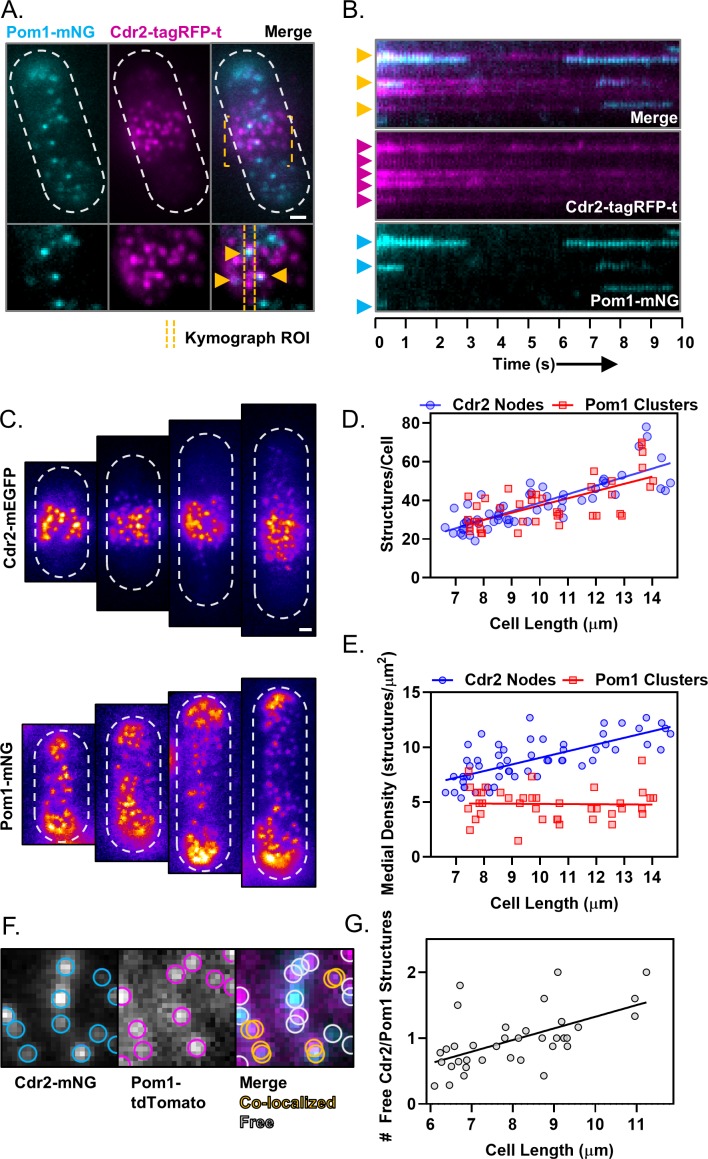
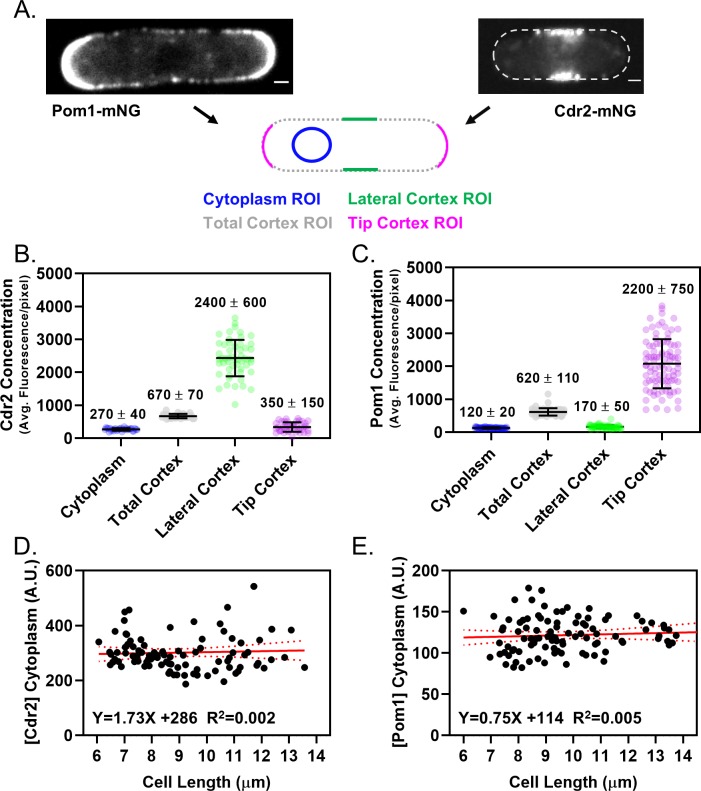
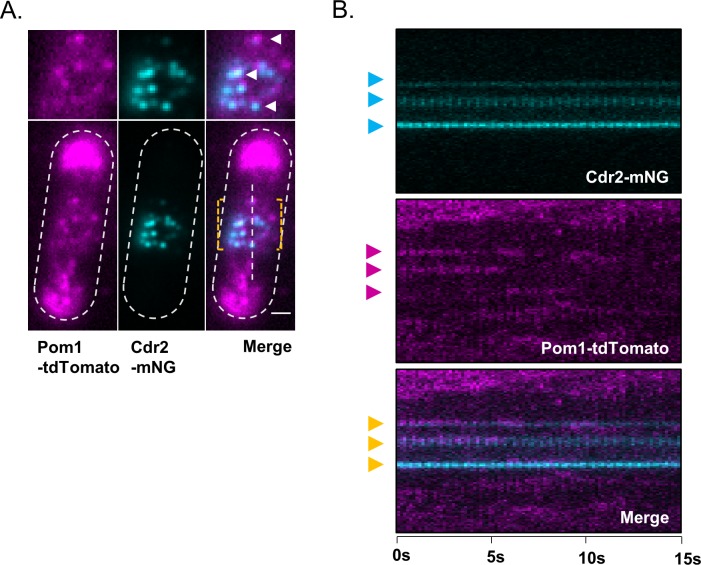
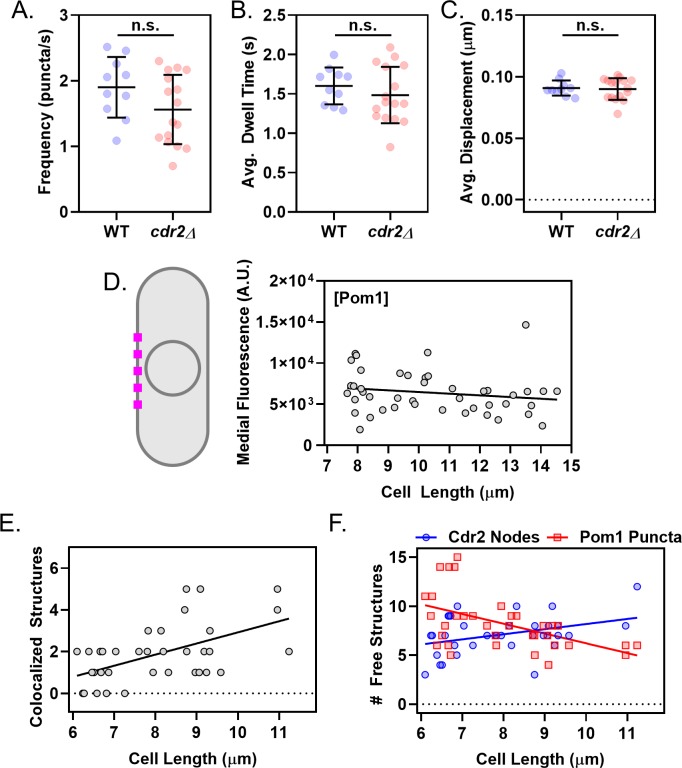
Figure 4. Size-scaling of Pom1 clusters and Cdr2 nodes at the lateral cell cortex.
(A) A subset of Pom1 clusters colocalize with Cdr2 nodes. Panels are TIRF microscopy images of cells expressing Pom1-mNG and Cdr2-tagRFP-t. Yellow dashed brackets outline the ROI of the lower zoomed panels. Orange arrows point to Pom1 clusters colocalized with Cdr2 nodes. Scale bar is 1 µm. (B) Kymographs generated using the ROI indicated in panel A. Cyan arrows indicate prominent Pom1 clusters, magenta arrows indicate prominent Cdr2 nodes, and orange arrows indicate colocalization. (C) Localization of Cdr2-mEGFP (upper panels) or Pom1-mNG (lower panels) in representative cells of increasing size, imaged by TIRF microscopy. Scale bar is 1 µm. (D) Total number of Cdr2-mEGFP nodes (blue circles) or Pom1-mNG clusters (red squares) measured per cell. Quantification is limited to clusters detected and resolvable in the TIRF illumination field. The slopes of the corresponding linear regressions are not significantly different (p=0.3757, n > 40 cells). (E) Density of Cdr2-mEGFP nodes (blue circles) or Pom1-mNG clusters (red squares) in 2 × 2 µm square ROIs at the cell middle, counted using TIRF microscopy. The slopes of the corresponding linear regressions are significantly different (p<0.0001, n > 40 cells). (F) Example of colocalization analysis for Pom1 clusters (magenta ROI) and Cdr2 nodes (cyan ROI) (left panels). Colocalized structures are marked with overlapping yellow ROIs, whereas non-colocalizing structures are marked with gray ROIs (right panel, gray circles). (G) Ratio of free Cdr2 nodes to free Pom1 clusters, plotted as a function of cell size. The slope of the linear regression is positive and significantly non-zero (p=0.0002, R2 = 0.33, n = 36 cells).