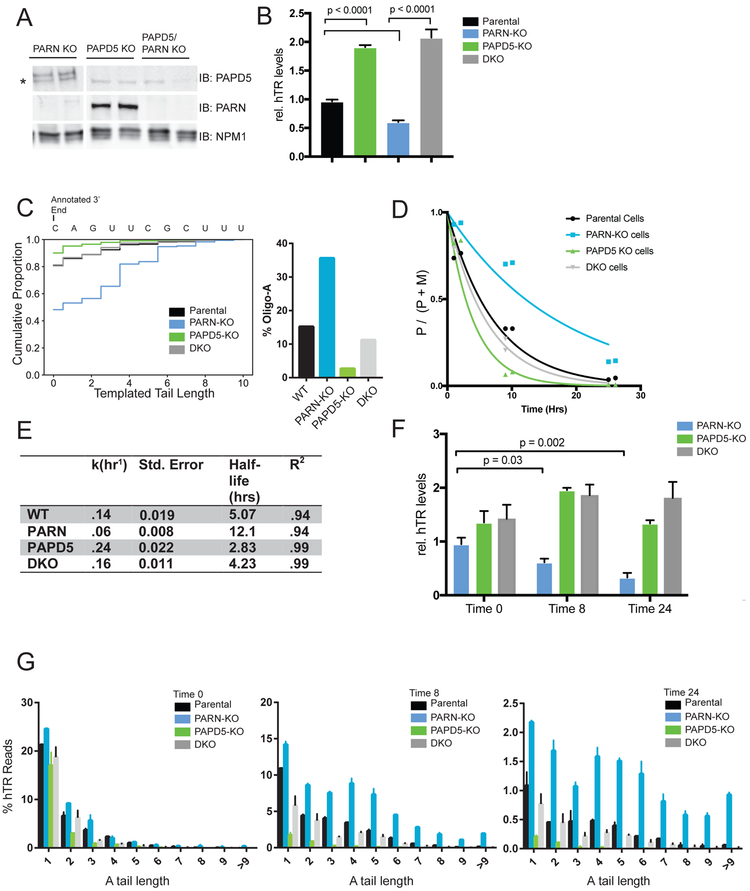
Figure 4: RNA processing enzymes PARN and PAPD5 define the rate of hTR precursor maturation.
A. Western blot for PARN and PAPD5 showing CRISPR-Cas9 KO of PAPD5, PARN, or PAPD5 and PARN (DKO). Unused KO clones are omitted. Asterisk (*) indicates background band
B. qRT-PCR of hTR relative to parental cells in parental, PARN-KO, PAPD5-KO, and DKO cells normalized to GAPDH. Error bars represent S.E.M.
C. 3’ RACE-Seq of steady-state hTR in indicated genotypes. Proportion of oligo-A molecules at steady-state for the indicated genotypes. hTR Reads≥20k
D. Exponential decay curves are fitted to the pulse chase data as in Figure 3F. For each time point, two biologic replicates are plotted. hTR Reads per time point≥13k.
E. Half-life measurements for maturation rate are calculated from curves in (D) using method from Figure 3G.
F. qRT-PCR of hTR relative to parental cells at indicated time points normalized to IVT luciferase spike-in.
G. Percent of hTR transcripts with the indicated oligo-A tail length is plotted for indicated genotypes for molecules at t0, t8, and t24. Error bars represent the S.E.M. from two biologic replicates. hTR Oligo-A reads: Parental≥1k, PARN-KO≥2.4k, PAPD5-KO≥0.3k, DKO≥1.3k.