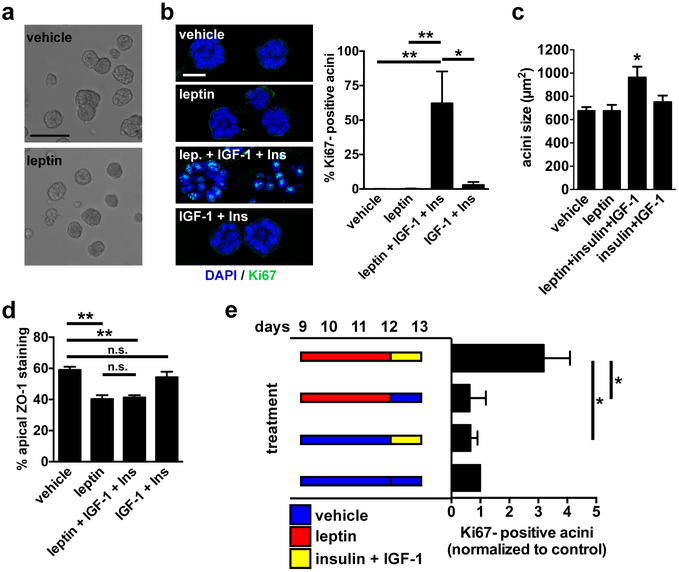
Fig. 5.
Leptin primes mammary epithelial cells for proliferation. a Bright field micrographs of differentiated S1 acini treated for 72h with vehicle or leptin. Scale bar, 100 µm. b Representative confocal images and quantification of Ki67 staining in acini treated for 72h with vehicle, with leptin (100 ng/ml), with IGF-1 (0.1 µg/ml) and elevated insulin (500 ng/ml), or with the combination of the three factors. Scale bar, 20 µm. *, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA and Tukey's; n = 5). c Sizes (cross sections) of acini treated as in B. *, P < 0.05 (compared to all other treatments, one-way ANOVA and Fisher’s LSD, n = 3). d Apical localization of ZO-1 in acini treated as in B. **, P < 0.01, n.s., P > 0.05 (one-way ANOVA and Tukey's; n = 3). e Analysis of Ki67 in S1 acini after treatments with leptin and growth factors. Treatments were dissociated in time, as indicated in the schematic. Values were normalized to control (vehicle/vehicle). *, P < 0.05 (Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s, n = 4).