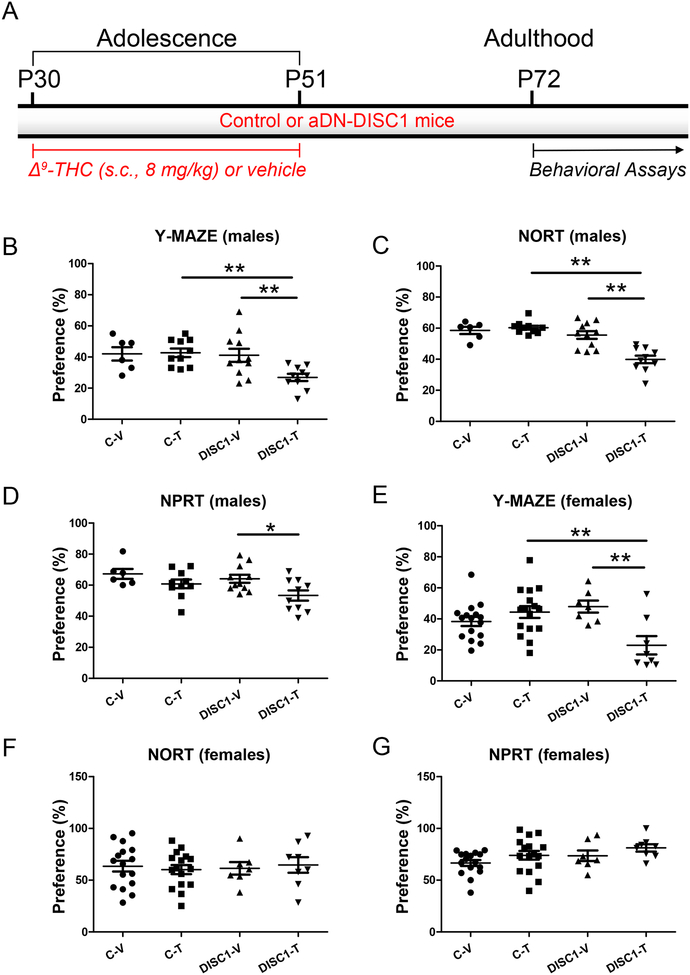
Figure 1. Cognitive impairments in astrocyte DN-DISC1 mice.
A - Schematic diagram of the treatment protocol
In all graphs the Y-axes depict the preference (%); the X-axes depict the experimental groups: C-V – control mice treated with the vehicle (6 males and 16 females); C-T – control mice treated with Δ9-THC (10 males and 16 females); DISC1-V – aDN-DISC1 mice treated with vehicle (11 males and 7 females); DISC1-T - aDN-DISC1 mice treated with Δ9-THC (10 males and 8 females)
Male mice
B- Spatial recognition memory in the Y maze. Compared to other groups, aDN-DISC1 male mice treated with Δ9-THC exhibited the significantly decreased preference for the previously blocked arm. Two-way ANOVA of the preference data revealed a significant effect of DN-DISC1, F(1,33)=5.49, p=0.025 and the significant aDN-DISC1 by Δ9-THC interaction, F(1,33)=4.46, p = 0.045; Fisher LSD post-hoc test showed that aDN-DISC1-Δ9-THC mice were significantly different from both C-T and DISC1-V mice, ** p<0.01.
C- Novel object recognition test (NORT). Compared to other groups, aDN-DISC1 male mice treated with Δ9-THC exhibited the significantly decreased preference for the novel object. Two-way ANOVA of the preference data revealed a significant effect of DN-DISC1, F(1,33)=26.12, p<0.001; a significant effect of Δ9-THC, F(1,33)=9.26, p=0.005 and the significant aDN-DISC1 by Δ9-THC interaction, F(1,33)=14.48, p<0.001; Fisher LSD post-hoc test showed that DN-DISC1- Δ9-THC mice were different from both C-T and DISC1-V mice, ** p<0.01.
D- Novel place recognition test (NPRT). Compared to other groups, aDN-DISC1 male mice treated with Δ9-THC exhibited the significantly decreased preference for the novel place of one of two identical objects. Two-way ANOVA of the preference data revealed a significant effect of Δ9-THC, F(1,33)=7.89, p=0.008. Planned post-hoc tests showed that significantly decreased preference in aDN-DISC1 mice treated with Δ9-THC compared to vehicle-treated aDN-DISC1 mice (DISC1-V) but there was no difference in the preference between Δ9-THC –treated- aDN-DISC1 (DISC1-T) and control (C-T) mice (p=0.074). * p<0.05.
Female mice
E- Spatial recognition memory in the Y maze. Compared to other groups, aDN-DISC1 female mice treated with Δ9-THC exhibited the significantly decreased preference for the previously blocked arm. Two-way ANOVA of the preference data revealed a significant effect of Δ9-THC, F(1,43)=4.74, p=0.035 and the significant aDN-DISC1 by Δ9-THC interaction, F(1,43)=12.88, p<0.001; Fisher LSD post-hoc test showed that aDN-DISC1-Δ9-THC (DISC1-T) mice were different from vehicle-treated - aDN-DISC1-vehicle (DISC1-V) mice and Δ9-THC -treated control (C-T) mice, ** p<0.01.
F- NORT. No group differences were found.
G- NPRT. No group differences were found.