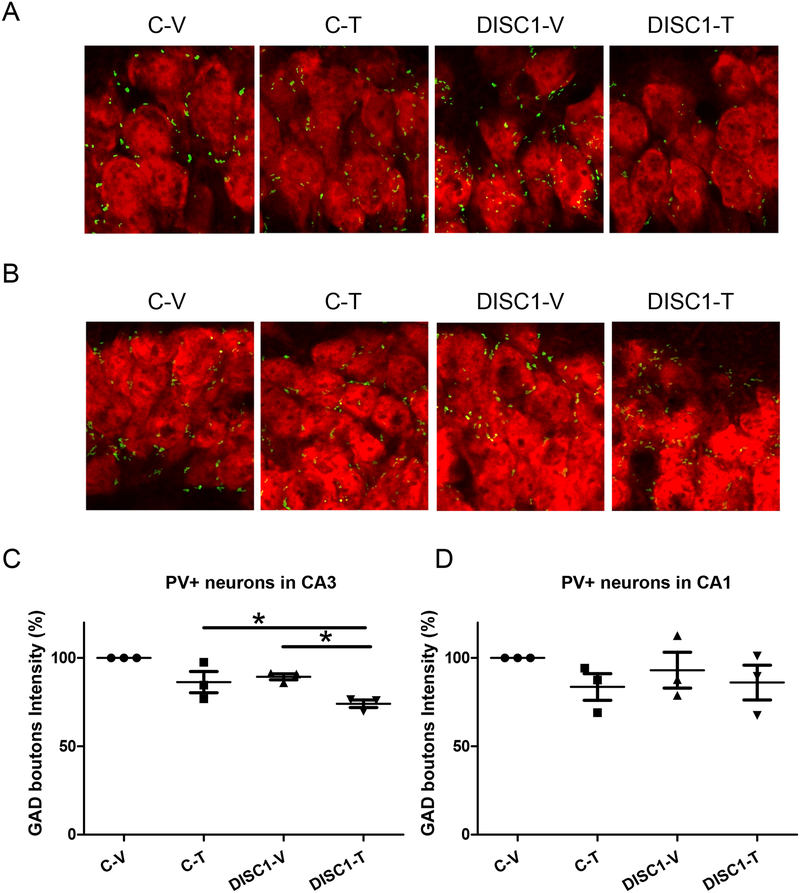
Figure 5. Astrocyte DN-DISC1 and Δ9-THC treatment synergistically decrease GAD+PV+ immunoreactivity in the CA3 area of the hippocampus.
On all data panels: the Y-axes depict the percentage of GAD boutons intensity in CA3 or CA1 PV neurons in relation to the level for the control-vehicle group; the X-axes depict the experimental groups (C-V – control mice treated with the vehicle; C-T – control mice treated with Δ9-THC; DISC1-V – aDN-DISC1 mice treated with vehicle; DISC1-T - aDN-DISC1 mice treated with Δ9-THC).
A- Representative images of GAD boutons intensity in pyramidal neurons of the CA3 area of the hippocampus; note decreased intensity in the DISC1+T group
B- Representative images of GAD boutons intensity in pyramidal neurons of the CA1 area of the hippocampus; note comparable intensity in all groups
C- Quantitative analyses of the intensity of GAD+PV+ presynaptic boutons around pyramidal neurons of the CA3 area of the hippocampus; n=3 sections per mouse, 3 mice per group; each data point represents one mouse. Two-way ANOVA of the intensity data revealed a significant effect of the group, F(1,8)=12.06, p=0.008 and significant effect of the Δ9-THC, F(1,8)=19.16, p=0.002; Fisher LSD post-hoc test showed that aDN-DISC1-Δ9-THC mice were significantly different from both C-T and DISC1-V mice, * p<0.05.
D- Quantitative analyses of the intensity of GAD+PV+ presynaptic boutons around pyramidal neurons of the CA1 area of the hippocampus. Two-way ANOVA of the intensity data revealed no significant effects of the DN-DISC1, F(1,8)=0.075, p=0.791, no significant effects of Δ9-THC, F(1,8)=2.129, p=0.183 and no DN-DISC1 by Δ9-THC treatment interaction, F(1,8)=0.347, p=0.572; N=3 sections per mouse, 3 mice per group; each data point represents one mouse.