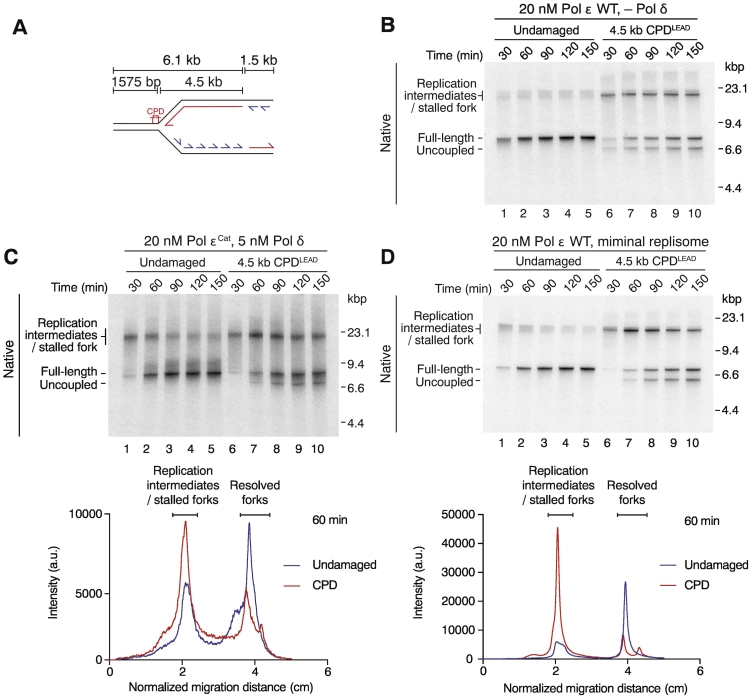
Fig. 4.
Cessation of leading-strand synthesis is a key mechanism underlying fork stalling and slowing. (a) Schematic of CPDLEAD templates used in panels b–d. (b and c) Replication reaction on undamaged and damaged templates in the absence of Pol δ (b) or in the presence of Pol δ and Pol εCat (c). Reactions contained 267 mM potassium glutamate, which prevents leading-strand synthesis by Pol α [15]). Lane profiles of replication products at 60 min are shown for the experiment in panel c. (d) Replication reactions performed on undamaged and damaged templates using the minimal replisome described in Ref. [15] but lacking Ctf4. Lane profiles of replication products at 60 min are shown. See also Supplemental Fig. S4.