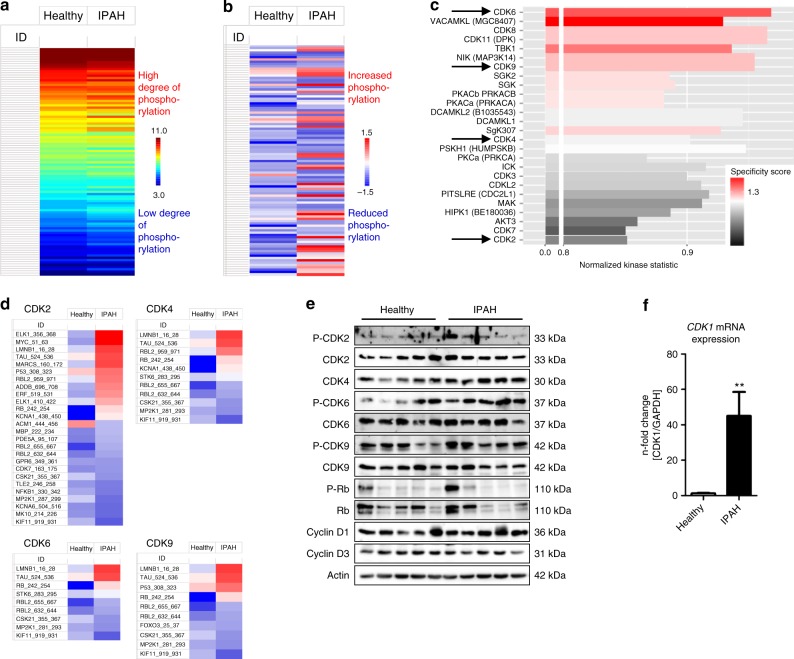
Fig. 1.
Kinome profiling reveals increased activity of the CDK-Rb-E2F signaling pathway in HPASMCs from IPAH patients. a Mean value of raw data for all individual samples, such as HPASMCs from healthy individuals (n = 5) and from IPAH patients (n = 6), presented as a heat map of log-transformed fluorescence signals upon substrate serine/threonine phosphorylation that are used to perform an upstream kinase analysis. b Mean value of a two-group comparison for all samples indicating the global changes in serine/threonine phosphorylation pattern between both HPASMCs entities under basal media conditions. c Bar chart displaying the overall prediction of kinases with higher activity in IPAH-patient-derived samples. Normalized kinase statistics is a mathematical-based algorithm indicating the estimated relative kinase activity while the specificity score reflects the reliability and accuracy of the prediction. d Two-group comparison for the four selected CDKs only including the phosphorylation pattern of their particular peptide substrate sets on the peptide array. e Western blot analysis for CDK2, CDK4, CDK6, and CDK9 activation and subsequent Rb-E2F downstream signaling in HPASMCs obtained from healthy donors and IPAH patients exposed to basal media. f CDK1 mRNA expression normalized to GAPDH as reference gene in HPASMCs of healthy individuals (n = 3) and IPAH patients (n = 3). After starvation, cells were cultured in basal media for 24 h. All data are presented as mean ± SEM of the n-fold change (2−∆∆Ct) compared with a healthy control and analyzed statistically using a Mann–Whitney test; **p < 0.01. Source data are provided as a Source Data file