Fig. 3.
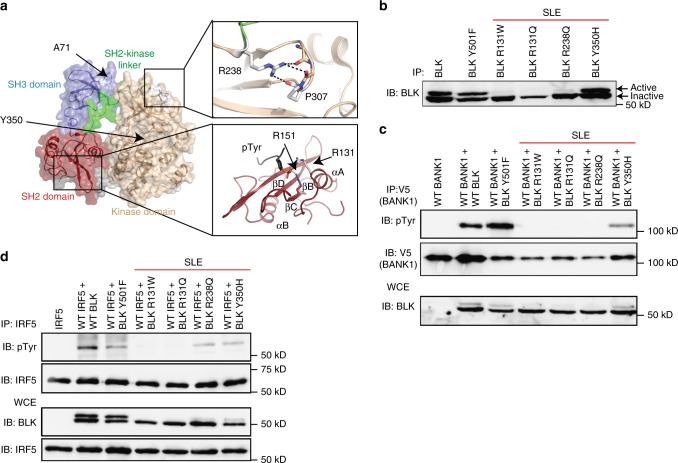
Rare and novel BLK variants are deleterious and impair kinase activity. a Modelled structure of the wild type BLK SH2 domain (PDB 1BLK) shown with a bound phosphotyrosine (pTyr) ligand (modelled from PDB 1 × 27). Arginine 131 (shown in white stick representation) is located on Helix ɑA (ɑA) and is known to co-ordinate phosphorylated tyrosine residues in a number of SH2 domain:ligand structures alongside the conserved R151 at helix ɑB (R151 in BLK, red stick representation). The other residues found to be altered in patients namely Y350 and R238, which interacts with P307, are also shown. Predicted polar contacts are shown as dotted lines. Beta-sheets are shown as ribbons with arrows and labeled βB-βC. Src Homolgy 3, SH2; Src Homology 3, SH3. b Anti-phosphotyrosine blotting of overexpressed and immunoprecipitated BLKWT, BLKY501F, and BLKR131W in HEK293T cells. The lower molecular weight band corresponds to the inactive form of BLK and the upper band to the active form. IP immunoprecipitation, IB immunoblot, WCE whole-cytoplasmic extract, SLE systemic lupus erythematosus. c Antiphosphotyrosine blotting of BANK1 after co-transfection of HEK293T cells with BANK1 and BLK expression vectors and pulldown of BANK1. pTyr phosphotyrosine, d Blotting of IRF5 after co-transfection of IRF5 and BLK variants in HEK293T cells indicates impaired phosphorylation of IRF5 by identified BLK variants. Blots in b–d are representative of at least three experiments