Fig. 3.
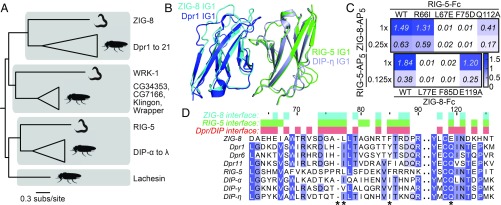
C. elegans ZIG-8 and RIG-5 bind each other using interface residues identified in Dpr-DIP complexes. (A) Phylogeny of Wirins in the two protostome model organisms, C. elegans and D. melanogaster. (B) The crystal structure of the ZIG-8–RIG-5 complex, superimposed with the Dpr1–DIP-η structure (11). The ZIG-8 N-terminal helix is removed from this view for clarity. (C) Mutations at the observed ZIG-8 and RIG-5 interface affect heterophilic binding. To effectively compare WT to mutants, protein concentrations within each mutant bait series (rows) were normalized. Each prey was tested at two concentrations to ensure that binding affinities are compared at nonsaturating concentrations. (D) Sequence alignments of IG1 domains of ZIG-8, RIG-5, Dprs, and DIPs. Asterisks indicate the four amino acid positions mutated in binding experiments.