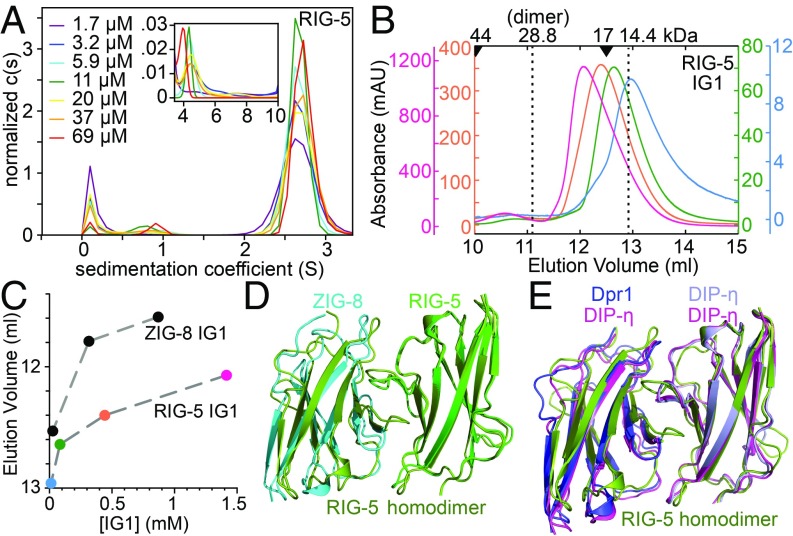
Fig. 4.
The IG1 domain of the C. elegans Wirins weakly homodimerize. (A) SV-AUC runs of the RIG-5 ectodomain show dimers (Inset) as a minor component in the micromolar range. For binding isotherms of RIG-5 and ZIG-8 homodimerization, see SI Appendix, Fig. S6 F and G. (B) RIG-5 IG1 elution volumes in size-exclusion chromatography decreases with increasing RIG-5 concentration, indicating a fast-exchange monomer-dimer equilibrium. Elution volumes for molecular weight standards are shown above as arrowheads. The RIG-5 IG1 construct used encodes for a ∼14.4-kDa mature glycoprotein. Absorbance was measured at a 0.2-cm path length. (C) Elution volumes plotted against loaded protein concentration indicate weak homodimerization for RIG-5 and ZIG-8, similar to what was observed for DIP-α and DIP-η (11). (D and E) Crystal structure of the RIG-5 IG1 homodimer superimposed with the ZIG-8–RIG-5 heterodimer (D) and with the Dpr1–DIP-η heterodimer and the DIP-η homodimer (E).