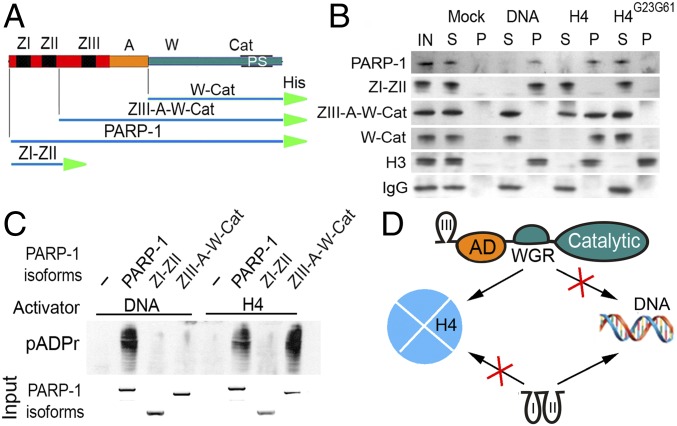
Fig. 3.
Histone H4-mediated PARP-1 activation is dependent on H4 binding to the C-terminal W-CAT domains of PARP-1. (A) Composition of deletional recombinant PARP-1 isoforms for in vitro experiments. His, 6 histidine tag. (B) In vitro binding assay (15): DNA, histone H4 and a mutant form of H4, H4G23G61 were each covalently coupled to CnBr beads and preincubated with a solution containing each deletional isoform of PARP-1. Following precipitation of beads, pellet (P) and solution (S) were subjected to PAGE and Western blot. The presence of PARP-1 isoforms in pellet and solution was detected on Western blot using anti–6XHis-tag antibody. Histone H3 was used as a positive control, which interacts with DNA and both forms of histone H4. IgG was used as a nonspecific protein-binding control. (C) In vitro activation assay. Sepharose beads with covalently attached DNA or H4 were preincubated with PARP-1 deletional isoforms and then mixed with NAD. The accumulation of pADPr was detected on Western blot using an anti-pADPr antibody. Input: the Coomassie Brilliant Blue stained PAGE gel shows the quantities of PARP-1 isoforms loaded in each reaction. (D) Diagram illustrating interactions between PARP-1 deletional isoforms and their targets (DNA and histones): ZIII-A-W-Cat (Top) interacting with H4-coupled beads only, ZI-ZII (Bottom) interacts with DNA-coupled beads but not with H4.