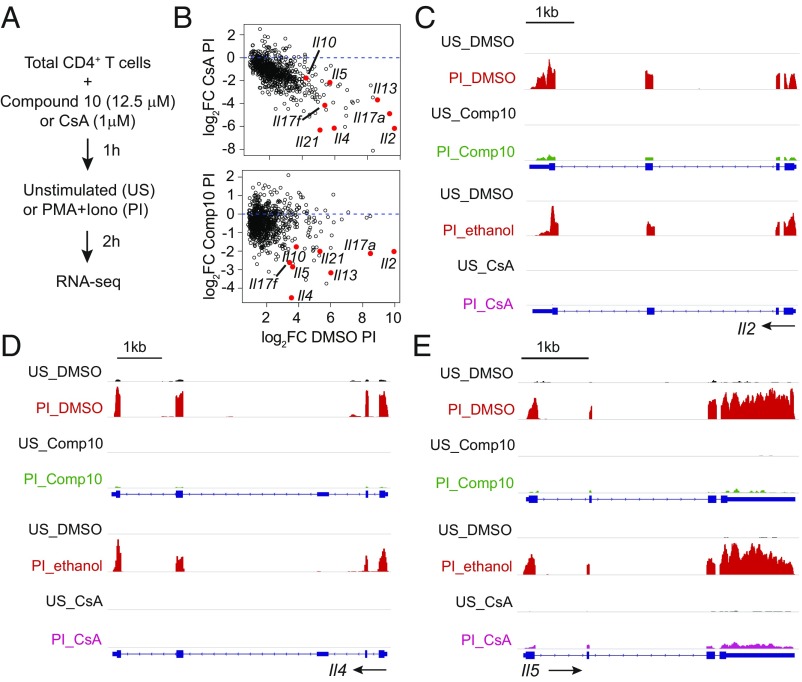
Fig. 7.
Comparing the effects of Compound 10 and CsA on T cell transcription. (A) Schematic representation of the RNA-seq assay. Total CD4+ T cells were preincubated with Compound 10 (12.5 μM) or DMSO for 1 h, or, in an independent experiment, with ethanol or CsA (1 μM) for 15 min, then left unstimulated (US) or stimulated with PMA (10 nM) and ionomycin (500 nM) (PI) for 2 h. (B) MA plots showing the effect of either CsA or Compound 10 on the genes that were induced by PMA and Ionomycin in both experiments. (C–E) Genome browser views of RNA-seq signals at the Il2, Il4, and Il5 loci in unstimulated (US) and stimulated (PI) conditions. The three genes were up-regulated by PMA+ionomycin in the vehicle control samples (DMSO or ethanol, red), and their up-regulation was inhibited in the presence of Compound 10 (green) or CsA (pink). Blue boxes correspond to exons, and arrows indicate the direction of transcription.