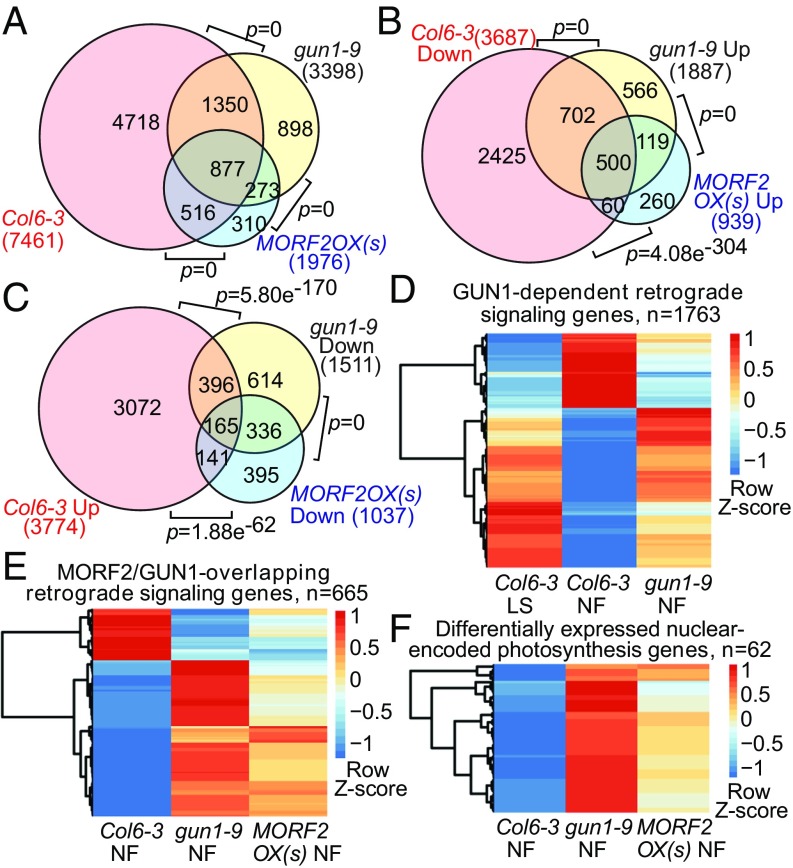
Fig. 3.
Transcriptome data indicate that MORF2OX(s) regulates nuclear gene expression similarly to gun1-9 during retrograde signaling. (A) The Venn diagram shows the differentially expressed gene overlap among Col6-3 (Col6-3 NF vs. Col6-3 LS), gun1-9 (gun1-9 NF vs. Col6-3 NF), and MORF2OX(s) [MORF2OX(s) NF vs. Col6-3 NF] under NF treatment. (B) The Venn diagram shows overlapped DEGs that are down-regulated in Col6-3 (Col6-3 Down) but have a higher expression level in gun1-9 (gun1-9 Up) and MORF2OX(s) [MORF2OX(s) Up] compared with wild type under NF treatment. (C) The Venn diagram shows overlapped DEGs that were up-regulated in Col6-3 (Col6-3 Up), but had a lower expression level in gun1-9 (gun1-9 Down) and MORF2OX(s) [MORF2OX(s) Down] than in the wild type under NF treatment. P values in A–C show the statistical significance of the overlap between two groups of genes in Venn diagrams. (D–F) The hierarchical clustering of expression levels of GUN1-dependent (D), MORF2/GUN1-overlapping (E) retrograde signaling genes, and differentially expressed nuclear-encoded photosynthesis genes (F) in different samples. LS, untreated; NF, NF-treated. Heatmaps show the Z-score value of log2-transformed [(average reads per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads) + 0.001] of each gene.