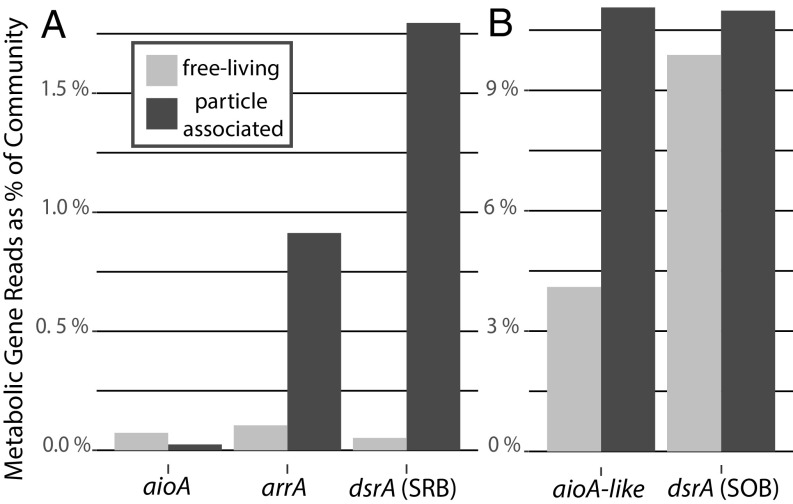
Fig. 4.
Arsenic respiratory genes and other related respiratory genes show niche partitioning in genomic contribution to microbial communities among free-living (<30 μm) or particle-associated niches (>30 μm) at 120-m depth in ETNP ODZ metagenomes. Reads identified using phylogenetically informed short-read placement. Contribution of reads presented as the length-normalized number of reads associated with each target gene/the number of length-normalized RNA polymerase B, rpoB, reads in the metagenomes * 100% to give an estimate of the gene’s % contribution to the overall microbial community metagenome (53). The relative proportion of a gene’s contribution to the microbial community when the free-living and particulate fractions are compared broken up into A with a much smaller proportion of the community containing arsenotrophy genes arsenite oxidase, aioA, and dissimilatory arsenate reductase, arrA, as well as the forward version of dissimilatory sulfite reductase, dsrA, which is involved in SRB. B shows a larger proportion of the community possesses the sequences aioA-like and the reverse version of dsrA which is involved in SOB.