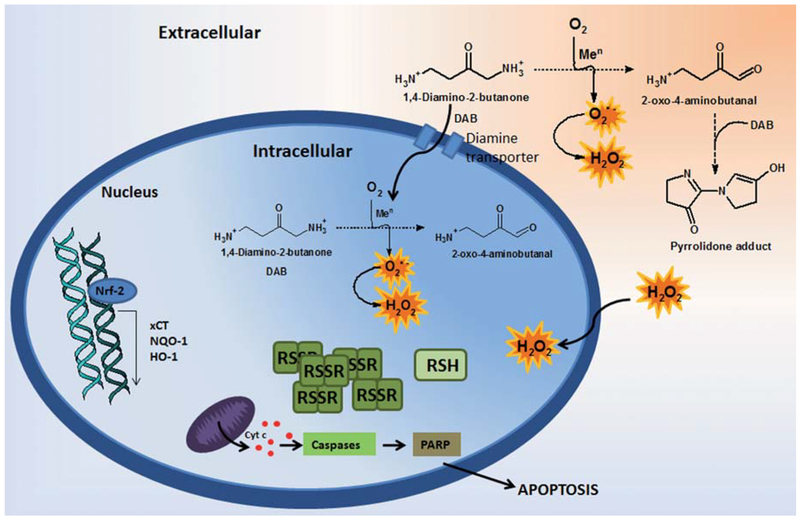
Figure 9. Envisaged mechanism to explain the cytotoxic effects of DAB on mammalian cells.
DAB undergoes metal-catalyzed aerobic oxidation yielding oxyradicals and an α-oxoaldehyde at both extra and intracellular environments. Increased ROS levels changes the cell redox balance leading to depletion of protective thiols. The resulting oxidizing triggers up-regulated stress response pathways such as Nrf-2, HO-1, NQO1 and xCT, as well as leading to activation of caspases cascades, PARP cleavage and subsequently apoptosis.