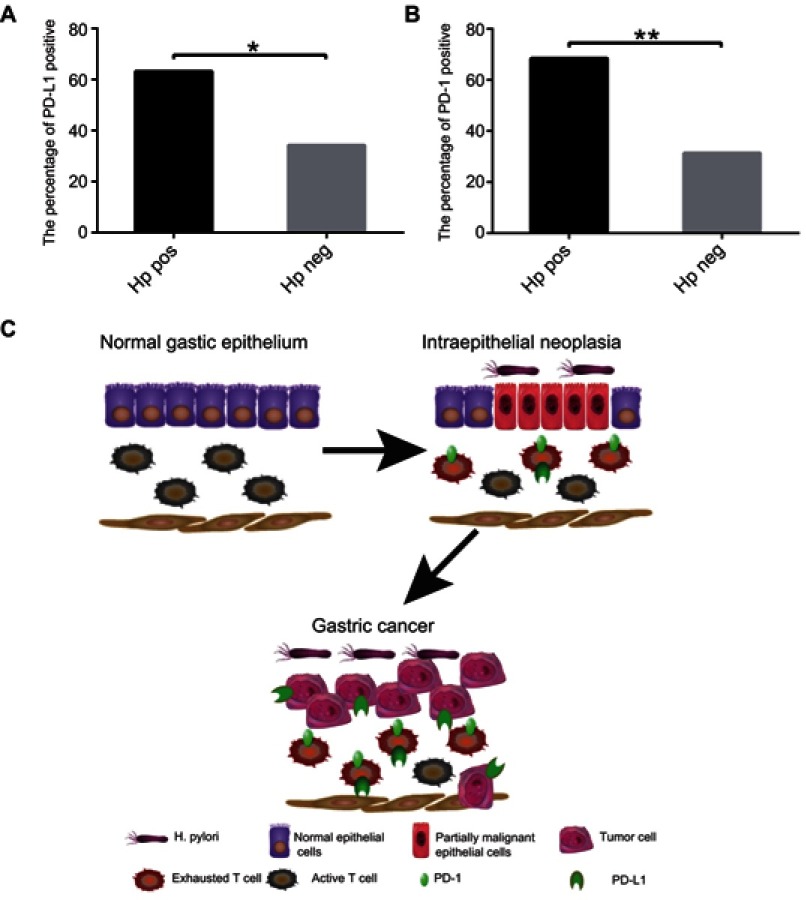
Figure 6.
The relationship between Hp infection and PD-1, PD-L1 expression. (A) The percentage of PD-L1 positive in patients with Hp positive and negative; (B) The percentage of PD-1 positive in patients with Hp positive and negative. (C) Pattern diagram: Under chronic infection caused by Hp, the immune system may cause excessive damage of normal tissues. In order to avoiding excessive damage, PD-L1/PD-1 checkpoint inhibition is upregulated, but also reduces the tumor killing effect of T-cells and promotes the progress of gastric cancer.
Note: *P<0.05 and **P<0.01.
Abbreviations: Hp, Helicobacter pylori; PD-1, programmed death-1; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1.