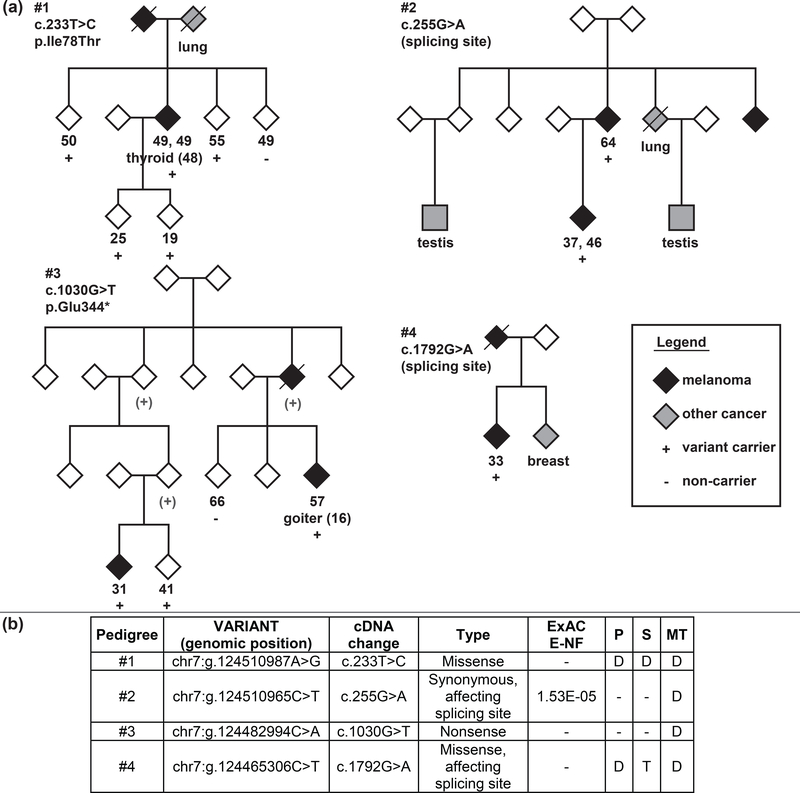
Figure 2. Pedigrees with POT1 variants and variant information.
a) Pedigree diagrams from families with rare POT1 germline variants. Gender has been hidden for family de-identification (except for individuals with gender-related cancer types). Below the symbol, age at diagnosis of each melanoma / age at blood sampling (for non-melanoma individuals), other cancer type / disease (age at diagnosis of other cancer/disease is indicated between parentheses) and presence “+” or absence “-” of the variant are listed. Non-tested obligated carriers are indicated as “(+)” in grey. b) Detailed information of the variant detected in each pedigree. ExAC E-NF: Variant frequency in European non-Finnish population from ExAC (http://exac.broadinstitute.org/) database. P: Polyphen2 functional prediction result (D=Probably damaging, PD=Possibly damaging, B=Benign) (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/). S: SIFT functional prediction result (D=Deleterious, T=Tolerated) (http://sift.jcvi.org/). MT: Mutation Taster functional prediction result (D=Disease Causing, N=Polymorphism,) (http://www.mutationtaster.org/)