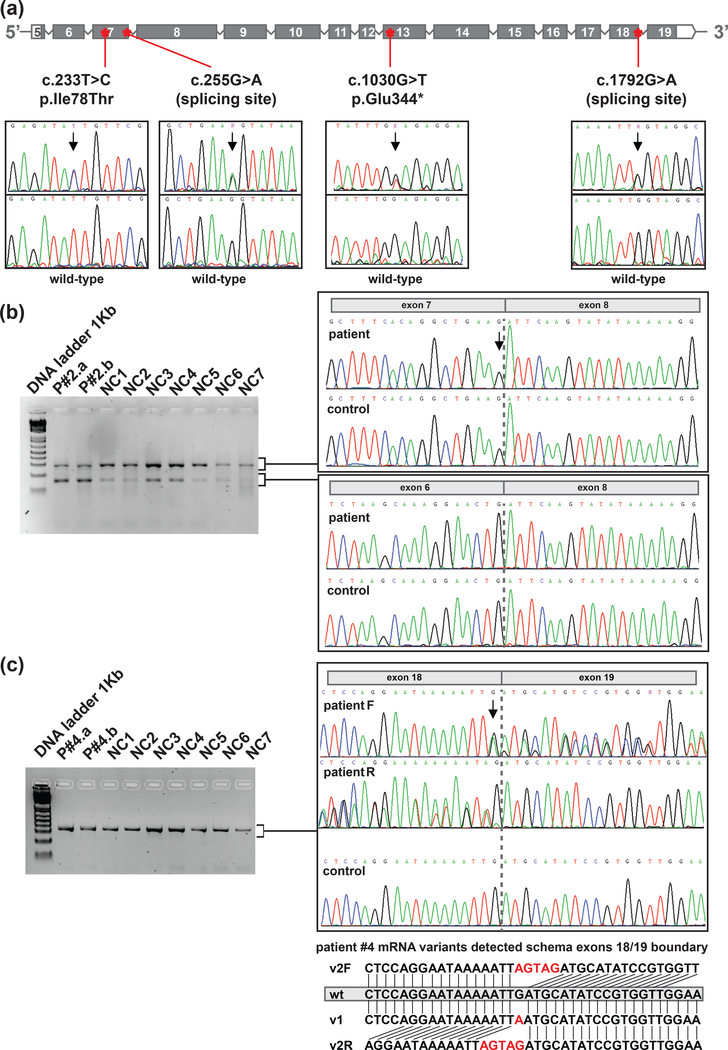
Figure 3. Rare POT1 germline variants.
a) Location of the variants within the gene context (coding exons according to ENST00000357628.7 transcript) and Sanger sequencing confirmation of the variants detected. The arrows spot the position of the genomic DNA change. b) Gel electrophoresis of cDNA amplification corresponding to the coding region between exons 5 and 8 in Patient #2 (germline variant c.255G>A) and 7 non-carriers (NC). Sanger sequencing of the fragments detected. Dotted grey line marks boundary between exons. c) Gel electrophoresis of cDNA amplification corresponding to the coding region between exons 17 and 19 in Patient #4 (germline variant c.1792G>A) and 7 non-carriers (NC). Sanger sequencing of the fragments detected. A schema of the different transcript alleles detected is shown (wt: wild-type r.1792G allele, v1: r.1792G>A allele and v2 (F=Forward; R=Reverse): r.1791_1792insAGTA).Two independent blood mRNA extractions were performed for each patient with mutation. P#2.a and P#4.a stands for sample A of patient number two and four, respectively. P#2.b and P#4.b stands for sample B of each patient.