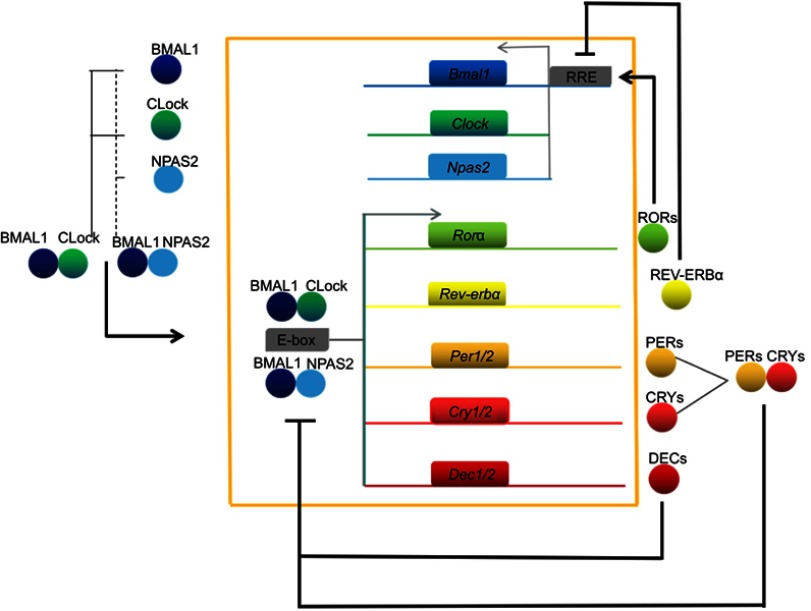
Figure 1.
Mammalian circadian clock network. BMAL1 proteins combine with CLOCK or NPAS2 to generate BMAL1:CLOCK or BMAL1:NPAS2 heterodimers, which cause transcriptional activation of core clock genes (for example, Per, Cry, and Dec) via a combination of E-box elements; this in turn inhibits BMAL1:CLOCK/NPAS2 dimer activity. Meanwhile, the BMAL1:CLOCK/NPAS2 dimers activate the transcription of the Rev-erbα and Rorα genes, and the resulting translated proteins promote and inhibit the transcription of Bmal1, respectively.
Abbreviations: Bmal1/BMAL1, Brain and muscle Aarnt-like protein 1; Clock/CLock, Circadian locomotor output cycles kaput k; Cry/CRY, Cryptochrome; Dec/DEC, Differentiated embryo-chondrocyte expressed; Npas2/NPAS2, Neuronal PAS domain protein 2; Per/PER, Period; Rev-erb, nuclear receptor subfamily; ROR, retinoid-related orphan receptor; RRE, ROR elements.