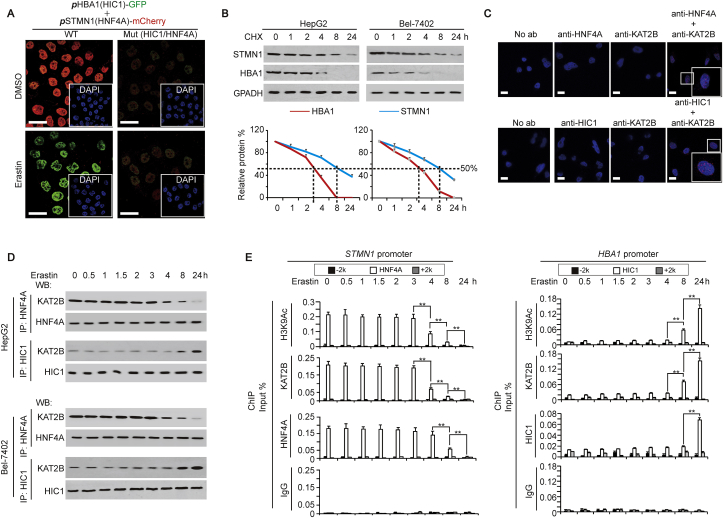
Fig. 6.
The balance between HIC1 and HNF4A controls FUF and FDF expression. (A) Representative IF images of HepG2 cells co-transfected with WT (containing HIC1 and HNF4A motifs) or Mut (with mutated HIC1 and HNF4A motifs) promoter reporter plasmids: pHBA1-GFP and pSTMN1-mCherry. The cells were treated with same amounts of DMSO or erastin (10 μM). The nuclei are also shown via staining with DAPI. Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) CHX chase experiments of STMN1 and HBA1 in HepG2 and Bel-7402 cells. The cells were harvested at the indicated time point after adding CHX (50 μg/ml). The ratios of STMN1 or HBA1 to GAPDH were also plotted. (C) PLA showing the interaction between HNF4A and KAT2B, and between HIC1 and KAT2B in HepG2 cells. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Interactions between HNF4A and KAT2B, and between HIC1 and KAT2B in HepG2 and Bel-7402 cells treated with erastin (10 μM) for indicating time, as demonstrated by co-IP using anti-HNF4A or anti-HIC1 antibodies for IP, and anti-KAT2B antibodies for WB. The HNF4A or HIC1 level in each co-IP samples was adjusted to the same content. (E) Modification of H3K9Ac, and enrichment of KAT2B and HNF4A at the indicated region around the STMN1 and HBA1 promoters in HepG2 cells treated with erastin (10 μM) for the indicated time. The data are shown as the means + SD from three independent experiments. **, p < 0.01 indicate statistical significance. The data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA test (Fig. 6B and E). Images of IF and WB are representative ones of 3 independent experiments (Fig. 6A–D).