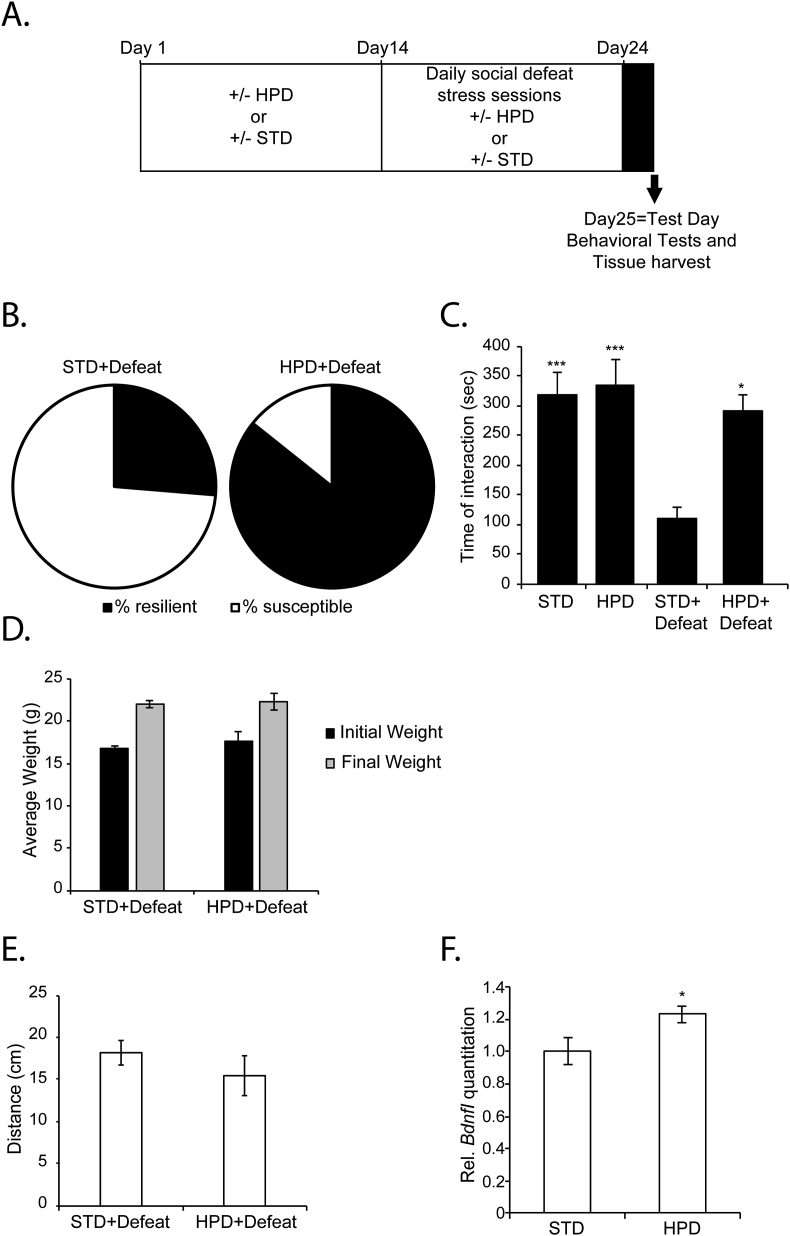
Fig. 5.
HPD promotes resilience to CSDS, rescues social avoidance behaviors and induces hippocampal Bdnf expression. (A) Animals were fed either STD or HPD for two weeks before being subjected to CSDS. Animals continued to receive the different diets during the CSDS. On day 24, behavioral tests and brain tissue collection were conducted. (B) HPD increase resilience to stress. In the group of mice (n = 19) receiving a STD and subjected to CSDS, 26% are resilient to stress. In the group of mice (n = 7) receiving a HPD and subjected to CSDS, 85.7% are resilient to stress. (C) HPD reverses the social avoidance phenotype as shown by the increase in the time spent in interaction zone of the social interaction test. Statistical significance was measured by 2way Anova followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. Interaction: F(1,43) = 4.886, p = 0.0324, Row Factor F(1,43) = 6.864, p = 0.0121 and column factor F(1,43) = 10.84, p = 0.02. STD + defeat vs HPD + Defeat: p = 0.0153, STD + defeat vs STD: p = 0.001 and STD + defeat vs HPD: p = 0.0002. (D) No significant changes in the weight were observed between the mice receiving a STD or HPD at the end of the experiment. (E) There was no significant difference in the distance travelled in the open field between the different mice groups. (F) Mice receiving a HPD for 4 weeks had significantly increased BdnfI expression levels as compared to mice receiving a STD. Statistical significance was measured by unpaired t-test groups. *p < 0.05. The n number for mice receiving STD and HPD is 10 and 12 respectively.