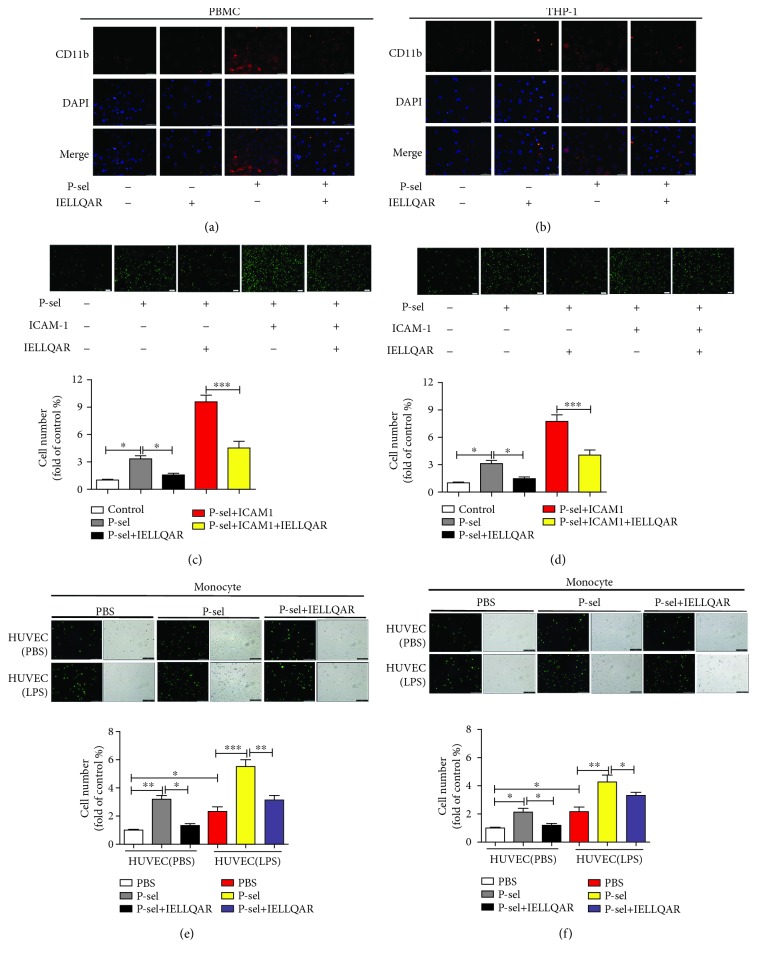
Figure 2.
IELLQAR inhibits the adhesion of P-selectin to monocytes and HUVECs. (a, b) PBMCs and THP-1 cells were incubated with PBS, 10 μg/mL of P-selectin, 10 μM IELLQAR, or 10 μg/mL of P-selectin plus 10 μM IELLQAR for 2 h, respectively. Then, the samples were incubated with anti-human CD11b Ab followed by Alexa Fluor® 555-conjugated rabbit Ab and fluorescence microscopy scanning. Scale bar: 50 μm. (c, d) Calcein-AM-labeled PBMCs and THP-1 cells were treated with or without 10 μM IELLQAR for 2 h. Dishes of parallel plate flow chambers were coated with P-selectin, P-selectin plus ICAM-1, or BSA overnight. Then, the cells were perfused through a microfluidic flow chamber at 2 dynes/cm2 shear stress for 5 min. Representative photographs of the adhesion of PBMCs and THP-1 cells. Scale bar: 100 μm. (e, f) Calcein-AM-labeled PBMCs and THP-1 cells were treated with PBS, P-selectin, or IELLQAR plus P-selectin for 2 h. HUVECs were activated or not by pretreating with 2 μg/mL of LPS for 6 h. Representative photographs of the adhesion of cells on HUVECs. Scale bar: 100 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001.