Figure 3.
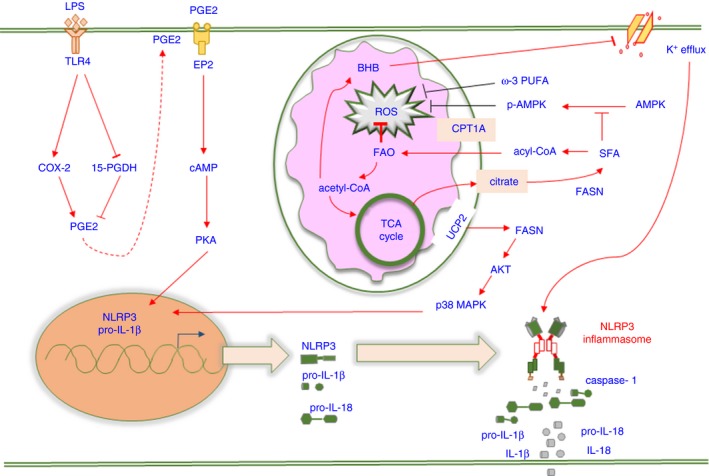
The signalling pathways involved in fatty acid metabolism‐regulated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Fatty acid metabolism involves fatty acid synthesis (FAS), fatty acid oxidation (FAO) and cholesterol metabolism. Saturated fatty acids (SFAs) and ω‐3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) exert opposite effects on NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and SFA enhances ROS generation by downregulating AMPK activity. Fatty acid synthase (FASN) induces NLRP3 and pro‐IL‐1β expression via the AKT/p38 MAPK axis. β‐Hydroxybutyrate (BHB) decreases NLRP3 inflammasome activation by inhibiting K+ efflux. An increased abundance of PGE 2 leads to pro‐IL‐1β expression via the EP2‐cAMP‐PKA axis.
