Figure 2.
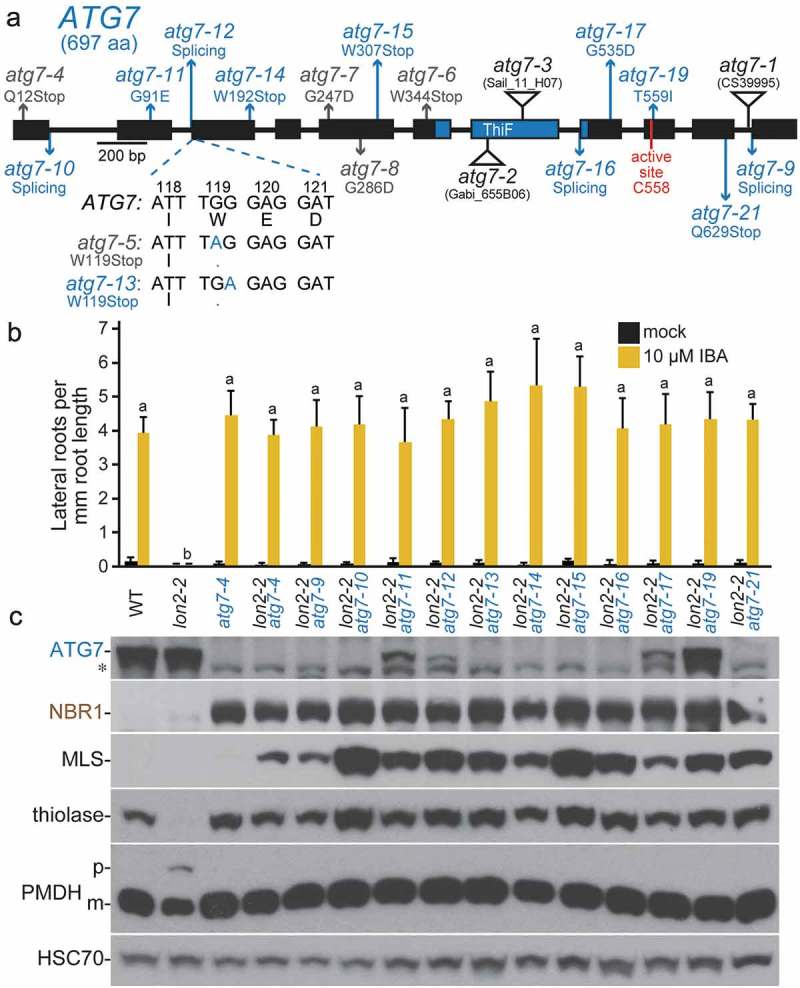
Numerous novel atg7 alleles recovered as lon2 suppressors. (a) Diagram of the ATG7 gene. Boxes and lines represent protein-coding regions and introns, respectively. The ThiF-like adenylation domain and active-site Cys residue are indicated. The positions of new atg7 mutations identified as lon2 suppressors are in blue; previously described EMS-derived lon2 suppressors [48] are in gray, and T-DNA insertion alleles [8,9,61] are indicated by triangles. atg7-9 is an unpublished allele (alias 8–30) from the pilot lon2-2 suppressor screen [48] that carries a g2959a mutation in the intron 10 splice acceptor site. The sequence of the atg7-13 nonsense allele compared to atg7-5 and wild-type ATG7 is shown below the gene diagram. aa, amino acids. (b) Lateral root density of 8-day-old wild type (WT), lon2-2, atg7-4, and lon2-2 atg7 seedlings grown without or with IBA. Error bars show standard deviations (n = 8). Statistically significant (P < 0.0001) differences determined by one-way ANOVA are depicted by different letters above the bars. (c) Extracts from 6-day-old seedlings were processed for immunoblotting with antibodies to the indicated proteins. The asterisk indicates a protein cross-reacting with the ATG7 antibody.
