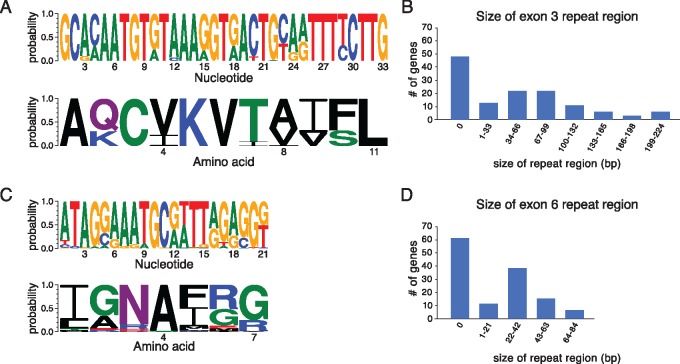
Fig. 3.
Expansion and contraction of repeat sequences contribute to rapid wtf gene evolution. (A) DNA (top) and amino acid (bottom) sequence logos representing the repeat region found in exon 3. (B) The distribution of exon 3 repeat region size across all assembled wtf genes. The sizes are presented in base pairs instead of repeat units because the terminal repeats are not always full length. (C) DNA (top) and amino acid (bottom) sequence logos representing the exon 6 repeat region found in many wtf genes. (D) The distribution of exon 6 repeat sizes in all assembled wtf genes.