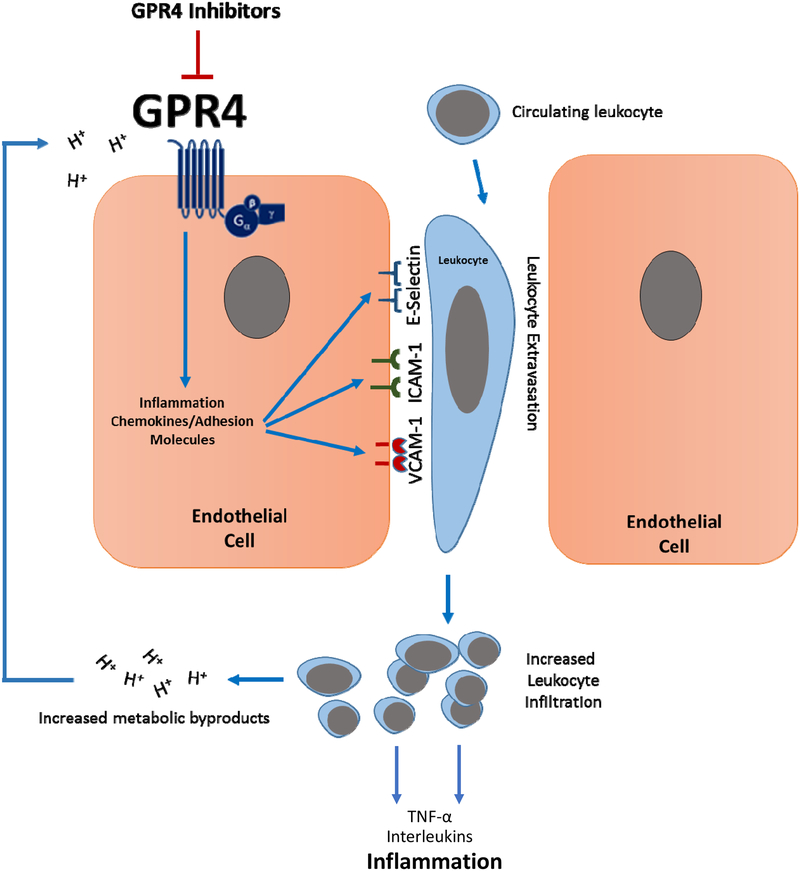
Fig. 7. Model of proposed mechanism of the anti-inflammatory action of GPR4 inhibitors.
GPR4 activation by protons in the extracellular milieu mediates the activation of vascular endothelial cells, the recruitment of immune cells and subsequent leukocyte extravasation into the inflamed tissue. Heavy immune cell infiltration into the inflammatory loci will result in further production of protons, as well as pro-inflammatory mediators, and subsequently maintain tissue inflammation and GPR4 activation. Inhibition of GPR4 activity by pharmacological intervention may present a novel approach to reduce inflammation by attenuating vascular endothelial cell activation and leukocyte infiltration into inflamed tissues.